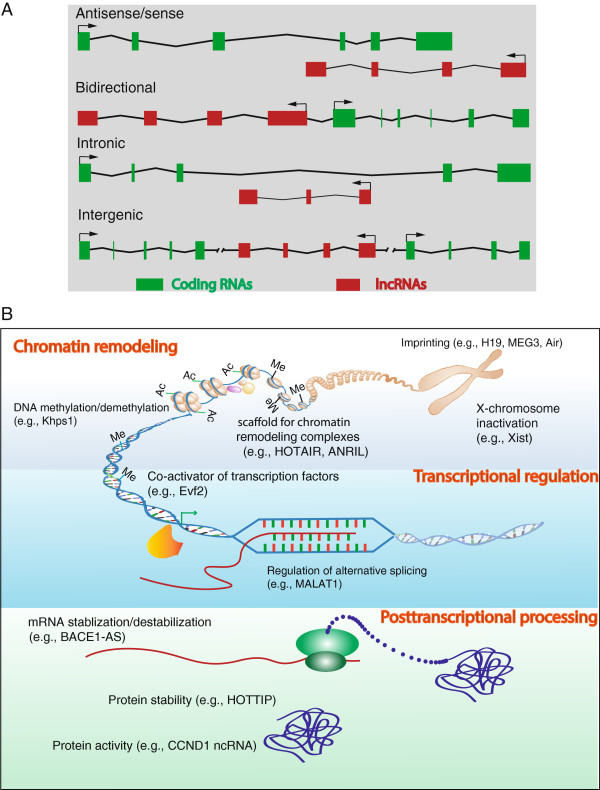
Figure 1.
Genomic structures and functions of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs). (A) Classification of lncRNAs according to their genomic locations relative to nearby protein coding genes: Antisense lncRNA— transcribed in the opposite direction of coding genes, and overlapped with a coding exon(s); Bidirectional lncRNA—transcribed from the promoter of a protein-coding gene and in opposite direction and, in general, within a few hundred base pairs; Intronic lncRNA—transcribed from inside of an intron of a protein-coding gene; Intergenic lncRNA—transcribed from between two protein-coding genes separated by a distance of five kilo base pairs. (B) Mechanisms of lncRNA function: lncRNAs regulate gene expression in a cis or trans manner via recruitment of proteins or molecular complexes to specific loci, scaffolding of protein complexes, titration of RNA-binding factors or as decoys, allowing other RNAs to start posttranslational regulation.