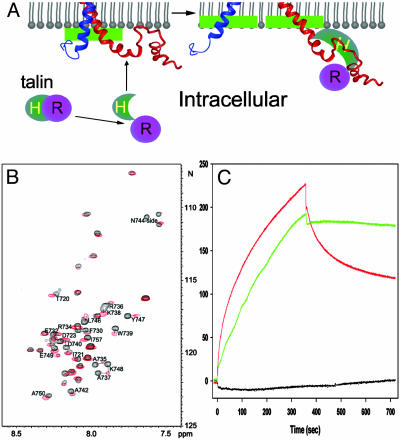
Fig. 5.
Structural illustration of integrin activation by talin. (A) A model for membrane-mediated change of cytoplasmic face during integrin activation. Agonist stimulation induces a conformational change in talin that exposes its head domain (Talin-H). Talin-H binds to the β3 tail at both the NPLY-containing region and the membrane-proximal helix. The binding to the membrane-proximal region displaces the αIIb tail from its complex with the β3 tail, leading to an unclasping, and the binding in the NPLY region releases a membrane-anchoring constraint on β3, which further facilitates the unclasping movement along the membrane surface. Notice the shifted membrane interface for both membrane-proximal helices before and after unclasping (green bars), which suggests a “fanning-out” unclasping process because the transmembrane domains may also undergo separation or open-scissor motion. The unclasping initiates the opening of the integrin C-terminal stalks, which is necessary for the rearrangement of the extracellular headpiece for high-affinity ligand binding. (B) HSQC spectra of the 15N-labeled β3 tail in the absence (black) and presence (red) of unlabeled talin F2-F3 at 35°C. Residues with significant chemical shift changes were labeled, which primarily involve membrane-proximal T720-D723 and C-terminal A735–A750, containing the N744-Y747 turn. (C) Surface plasmon resonance data. One hundred nanomol of talin-H (1–429) was passed over CM5 sensor chips coated with β3 (716–762) (red), a β3 membrane-proximal mutant (H722A/D723A, black), or a β3 single mutant (F730A, green), with association and dissociation phases of 360 sec. The former mutant had diminished binding to talin, but the latter has about the same as the binding capacity to talin, indicating that H722D723 is critical for talin binding. D723A/R724A mutations also had the same effect as H722A/D723A (data not shown). Talin-H made no detectable interaction with αIIb(989–1008) when this peptide was coupled to a CM5 chip.