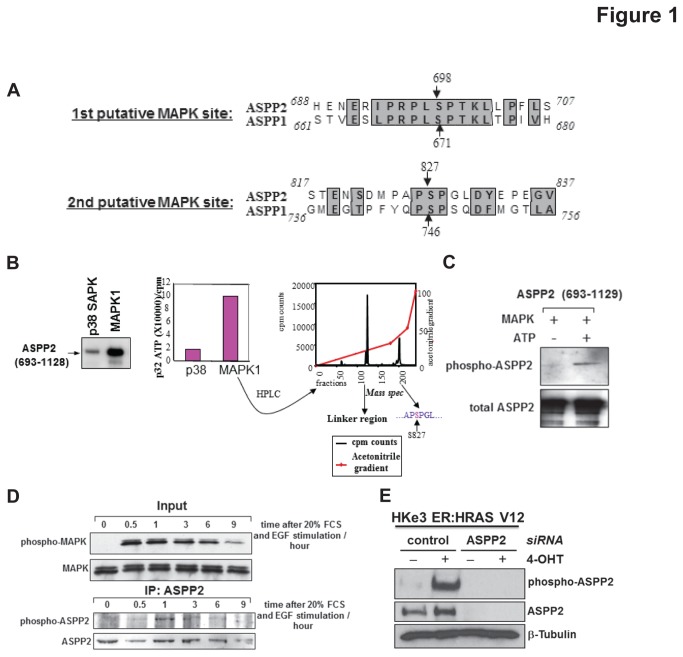
Figure 1. MAPK phosphorylates ASPP2.
(A) ASPP1 and ASPP2 have two conserved putative MAPK2 phosphorylation sites in their C-terminus. (B) The C-terminus fragment of ASPP2 is phosphorylated in vitro by MAPK1 (left panel). The intensity of phosphorylation is quantified (middle panel). The MAPK1 phosphorylated ASPP2 fragment was digested with trypsin and chromatographed and the radioactive peptides were measured by mass spectrometry (right panel). The first peak represents the GST linker region whereas the second presented a region of equal mass to the fragment containing serine 827. (C) An in vitro phosphorylation assay was performed on the ASPP2 C-terminus fragment with recombinant MAPK1 and non-radioactive ATP. The phosphorylation status of ASPP2 was assessed using the purified NGH.S4 phospho-specific ASPP2 antibody (upper panel). Total ASPP2 is shown in the lower panel. (D) Saos2 cells were starved then stimulated with serum and EGF. At the indicated times the cells were harvested and either blotted for phospho/total MAPK (upper panel) or immunoprecipitated for total ASPP2 and blotted with NGH.S4 phospho-ASPP2 antibody. (E) Total cell lysates from HKe3 ER:HRASV12 cells treated with or without 4-OHT were transfected with control siRNA or siRNA against ASPP2. ASPP2 phosphorylation was detected with ES1 phospho-ASPP2 antibody and total ASPP2.