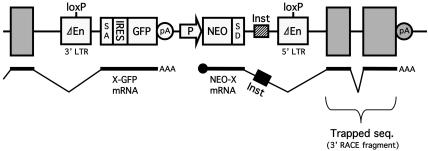
Fig. 1.
Structure of a variant of the RET gene trap vector. The vector uses an improved poly(A) (pA) trap strategy for the efficient identification of functional genes regardless of their expression status in target cells (13). Gray rectangles represent exons of the trapped gene X. A cDNA fragment of the trapped gene is retrieved as a 3′ RACE product by amplifying the downstream portion of the NEO-X fusion transcript. ΔEn, enhancer deletion; SA, splice acceptor; IRES, internal ribosome entry site; P, mouse RNA polymerase II gene promoter (long form); SD, splice donor; Inst, mRNA instability signal derived from the human granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor gene; X-GFP and NEO-X mRNAs, fusion transcripts generated from the 5′ half of the trapped gene X and the GFP cassette, and the NEO cassette and the 3′ half of the gene X, respectively.