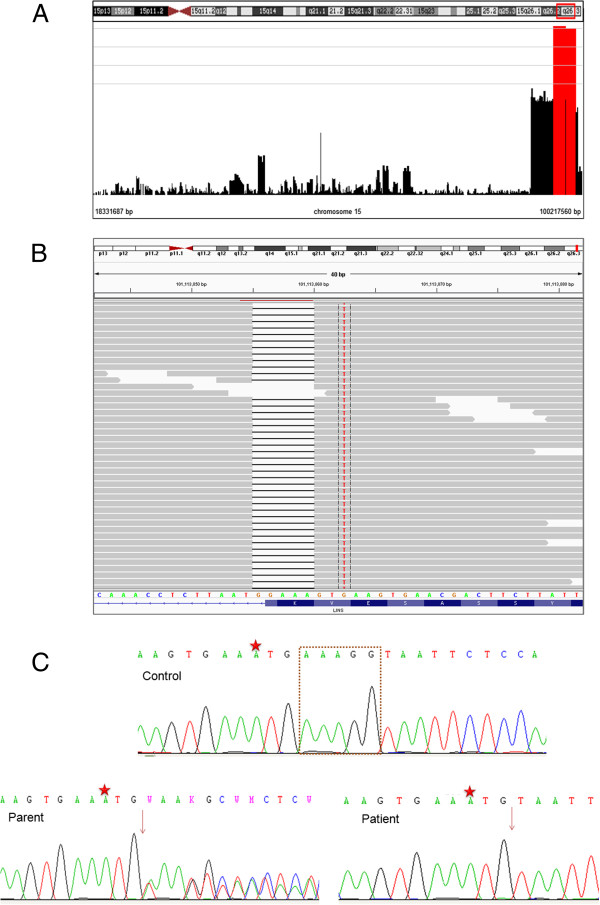
Figure 2.
Genomic mapping and genetic testing of an autosomal recessive intellectual disability phenotype. A. Genotyping the whole genome of both parents (I1 and I2) and affected children (II1 and II2) detected a homozygosity on chromosome 15q26. B. Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV) visualization of homozygous mutation c.1219_1222+1delAAAGG in LINS gene from exome data. All reads show 5 bp deletion, sequence of wild type gene and exon annotation at bottom. The adjacent homozygous substitution G>A (C>T on reverse strand) is a common variant rs12719734G>A. C. DNA sequencing chromatograms confirmed the segregation of the AAAGG (inside the brown square) deletion detected by exome data with the assessed phenotype. The deletion was found to be homozgous in the patients (II1 and II2) and heterozygous in parents (I1 and I2). The deletion was not found in 100 normal controls. The rs12719734G>A (designated with a red star) was found in all the screened individuals.