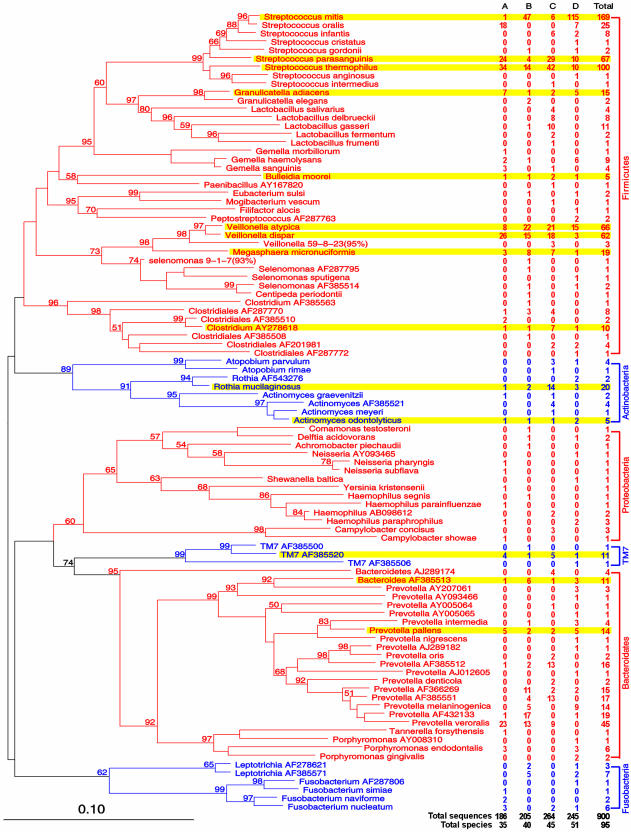
Fig. 3.
Phylogenetic analysis of bacterial 16S rDNA detected in biopsies of the normal distal esophagus from four persons. Sequences were aligned by using sequence aligner at RDP II. Misaligned positions were corrected by using arb. Phylogram was generated by using paup 4.0b10 neighbor-joining analysis, based on HKY85 distance matrices. Bootstrap values (based on 500 replicates) are represented at each node when >50%, and the branch length index is represented below the phylogram. Names of SLOTU are located at the termination of each branch. 16S rDNA clones are potential bacterial species whose phylogenetic positions were designated by PCR-amplified 16S sequences only, represented by the closest genus, followed by the GenBank accession number of the best-matched sequence. Unknowns are represented by the closest taxon followed by the serial number of the clone used in this study, as well as the percent sequence identity (in parentheses). The frequency at which a species was detected and its sources are indicated (on the right). The 95 SLOTU belonging to six phyla, contrasted by alternating red and blue print, are shown (on the right). SLOTU shared by all four persons are highlighted in yellow.