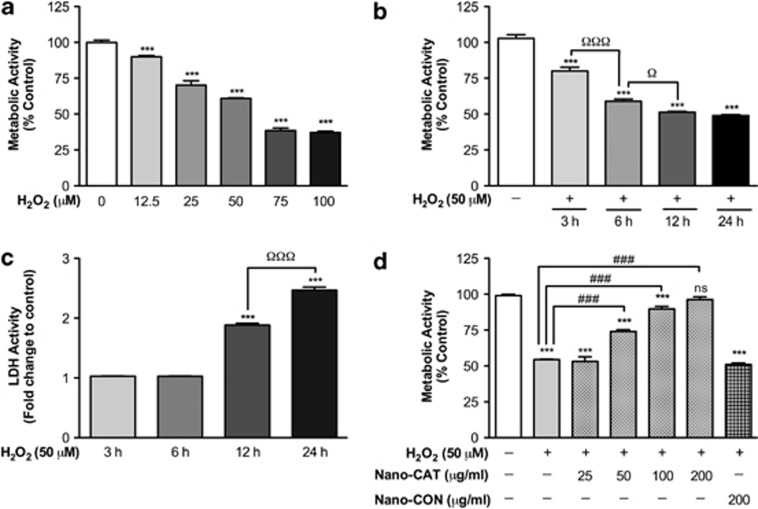
Figure 2.
Demonstration of H2O2-mediated neurotoxicity and Nano-CAT-mediated protection. Primary human neurons were exposed to H2O2 (12.5–100 μM) for increasing time points (3–24 h). Metabolic activity was measured by MTT assay and expressed as a percentage of MTT activity (a, b). A dose- and time-dependent decrease in cell viability was observed (a, b). The cell membrane integrity was measured by LDH assay as fold increase over the respective control (c). Human neurons were exposed to H2O2 (50 μM) with or without Nano-CAT (50–200 μg/ml) or Nano-CON (200 μg/ml) (d) Cell survival was analyzed after 6 h by MTT assay as expressed as a percentage of MTT activity (d). Data are mean ±S.E.M. of a minimum of triplicates and representative of at least three biological replicates. Symbols indicate the relative level of significance compared with vehicle control (***P<0.001) or with the H2O2-treatment group (ΩP<0.05 and ΩΩΩP<0.001) or with H2O2 alone (ns, not significant; ###P<0.001)