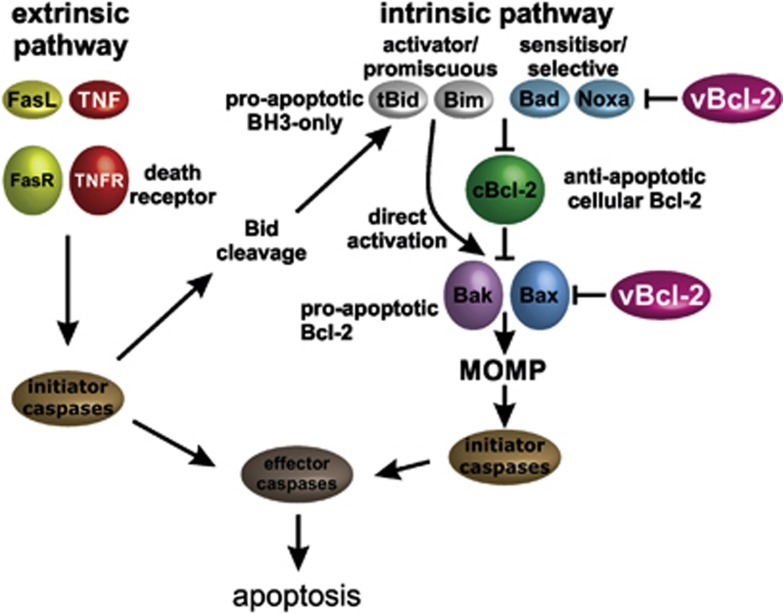
Figure 1.
Points of intervention of viral Bcl-2 proteins in mammalian Bcl-2-regulated apoptosis. Shown is a simplified schematic view of apoptosis induction in mammalian cells and its inhibition by pro-survival viral Bcl-2 (vBcl-2) proteins. Apoptosis may be initiated by activation of cell surface receptors (extrinsic apoptosis or death receptor-initiated apoptosis7) or by intracellular mechanisms (‘intrinsic' or mitochondrial pathway). In either case, a proteolytic cascade of caspases is initiated that destroys the cell. A network of interactions between Bcl-2 proteins controls mitochondrial membrane integrity. BH3-only proteins may either inhibit pro-survival proteins or activate the two key Bcl-2 family members, Bax and Bak, to disrupt the mitochondrial outer membrane and release caspase-activating factors. Viral Bcl-2 proteins bind Bax or Bak or BH3-only proteins to prevent apoptosis induction. cBcl-2, cellular Bcl-2