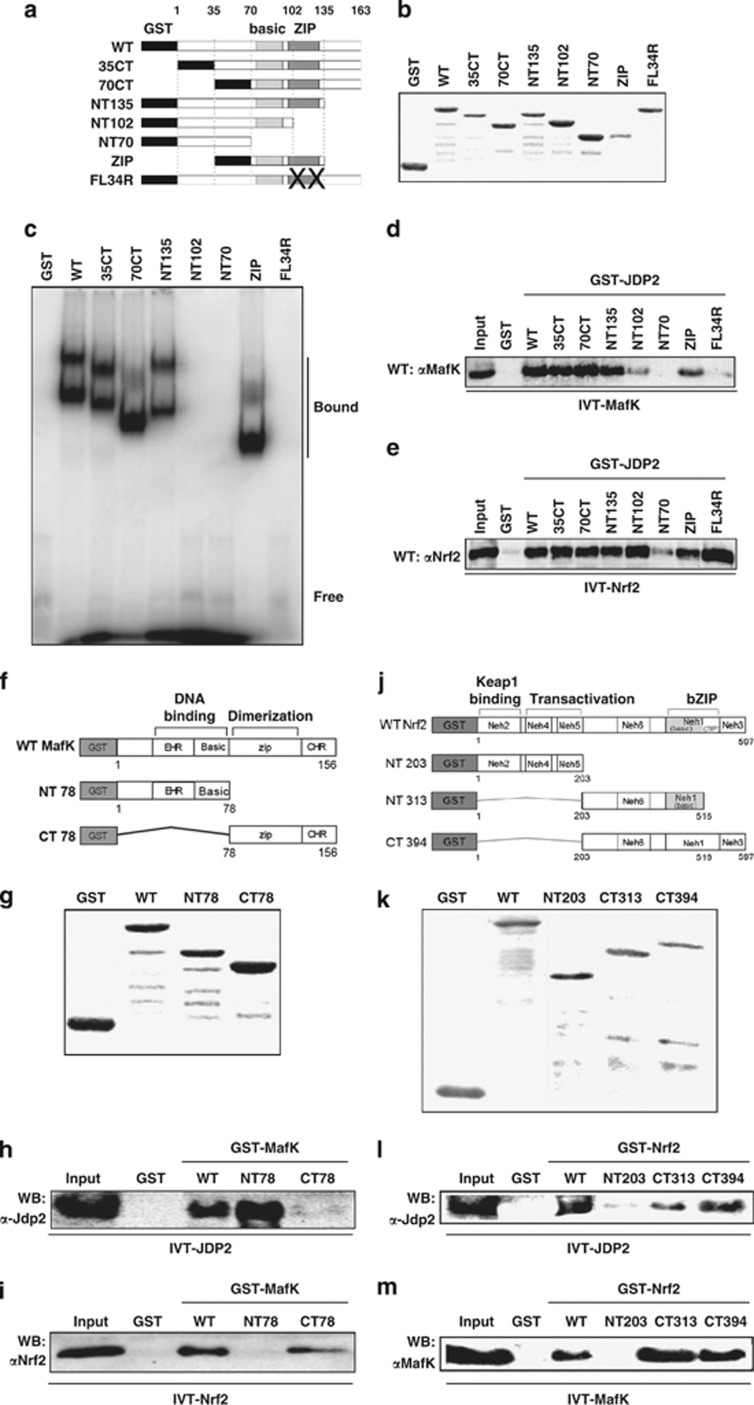
Figure 4.
Reciprocal interaction of JDP2, Nrf2 and MafK in vitro. (a) The structure of GST–JDP2 proteins used for EMSA assay in vitro. The structures of various mutant forms of JDP2 are shown below. (b) Expression of the GST–JDP2 proteins. The GST–JDP2 proteins were detected on 10% SDS-PAGE after purification with GST affinity resins. (c) EMSA assay of the JDP2 deletion mutants with human NQO1–ARE. EMSA assay was performed using a series of deletion mutants of the Jdp2 protein, as indicated in Materials and Methods. The upper bands of the DNA–protein complexes seem to be dimer forms. (d) The bZIP domain of JDP2 is recruited and binds MafK. The full-length rat MafK (in vitro-translated MafK; IVT–MafK) was expressed using an in vitro transcription–translation system without [35S]-methionine as recommended in the manufacturer's protocol. Affinity-resin-purified GST or GST–JDP2 fusion variant proteins were mixed with IVT–MafK. The bound MafK was applied to SDS-PAGE and immunodetected using a MafK-specific antibody. (e) The basic domain of JDP2 is recruited and binds Nrf2. The IVT–Nrf2 protein was incubated with GST–JDP2 and a protein-binding assay was performed as described in c. (f) The structure of mutant forms of various GST–MafK proteins used for EMSA assay in vitro. (g) Expression of the GST–MafK proteins. The GST–MafK was detected on 10% SDS-PAGE after purification with GST affinity resins. (h) The DNA-binding domain of MafK is recruited and binds JDP2. The full-length mouse JDP2 (IVT–JDP2) was expressed, using an in vitro transcription–translation system without [35S]-methionine, as recommended in the manufacturer's protocol. Affinity-resin-purified GST or GST–MafK fusion variant proteins were mixed with IVT–JDP2. The bound JDP2 was applied to SDS-PAGE and immunodetected using a JDP2-specific antibody. (i) The ZIP domain of MafK is recruited and binds Nrf2. The structure and expression of GST–MafK and IVT–Nrf2 were described above. The bound Nrf2 was immunodetected using an Nrf2-specific antibody. (j) The structure of various mutant forms of the GST–Nrf2 protein used for EMSA assay in vitro. (k) Expression of the GST–Nrf2 protein. The GST–Nrf2 proteins were detected on 10% SDS-PAGE after purification with GST affinity resins. (l) The C-terminal and half-bZIP domain of Nrf2 are recruited and bind JDP2. The full-length mouse JDP2 (IVT-Jdp2) was expressed using an in vitro transcription–translation system without [35S]-methionine. GST or GST–MafK fusion proteins were mixed with IVT–Jdp2. After washing, bound proteins were applied on SDS-PAGE and immunodetected using a Jdp2-specific antibody. (m) The bZIP and Neh 6 domains of Nrf2 are associated with MafK. The IVT–MafK protein and GST–Nrf2 proteins were incubated and the bound MafK was immunodetected using a MafK-specific antibody