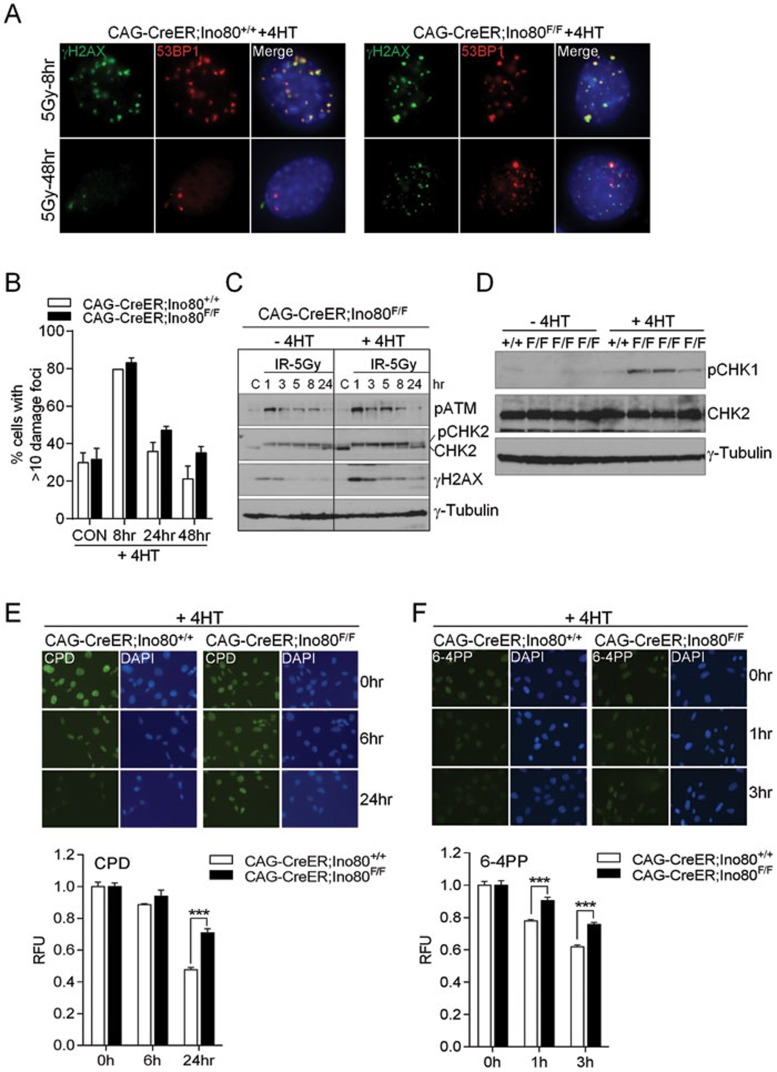
Figure 3.
Impact of mIno80 deletion on DNA damage signaling and repair. (A) Immunostaining for γ-H2AX- and 53BP1-positive DNA damage foci in CAG-CreER; mIno80+/+ and CAG-CreER; mIno80F/F MEFs treated with 4-HT, 8 or 48 h following 5 Gy IR exposure. (B) Quantification of A for percent of cells containing >10 γ-H2AX or 53BP1 foci. An additional time point at 24 h post IR exposure is included. (C) Immunoblot showing amount of phospho (p)-ATM, total and p-CHK2, γ-H2AX, and γ-tubulin present in CAG-CreER; mIno80F/F MEFs with or without 4-HT treatment, harvested at 1, 3, 5, 8, 24 h after exposure to 5 Gy IR. C: unirradiated controls. (D) Immunoblotting for p-CHK1, total CHK2, and γ-tubulin levels in CAG-CreER; mIno80+/+ and CAG-CreER; mIno80F/F MEFs with or without 4-HT treatment for 96 h. (E, F) Immunostaining of CPD (E) and 6-4PP (F) in CAG-CreER; mIno80+/+ and CAG-CreER; mIno80F/F MEFs treated with 4-HT. For CPD staining, cells were fixed at 0, 6, or 24 h after irradiation with 5 J/m2 of UV (254 nm). For 6-4-PP staining, cells were fixed at 0, 1, and 3 h after 20 J/m2 of UV (254 nm) exposure. Quantifications of DAPI-normalized CPD or 6-4PP signals are shown in the lower panels. Error bars represent s.d. derived from more than six independent data points. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences (***P < 0.0001, Student's t-test).