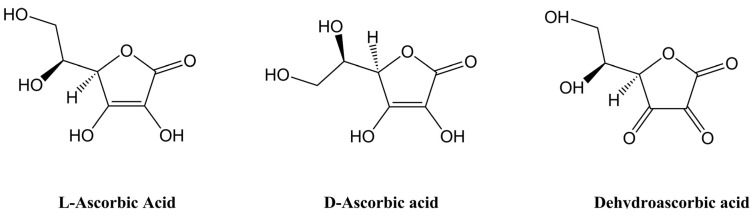
Figure 1.
Vitamin C in its reduced form (ascorbic acid), shown as both its l- and d-isomers, and its two electron oxidation form (dehydroascorbic acid, DHA). DHA can be readily reduced back to ascorbic acid in vivo via both chemical and enzymatic pathways [23].