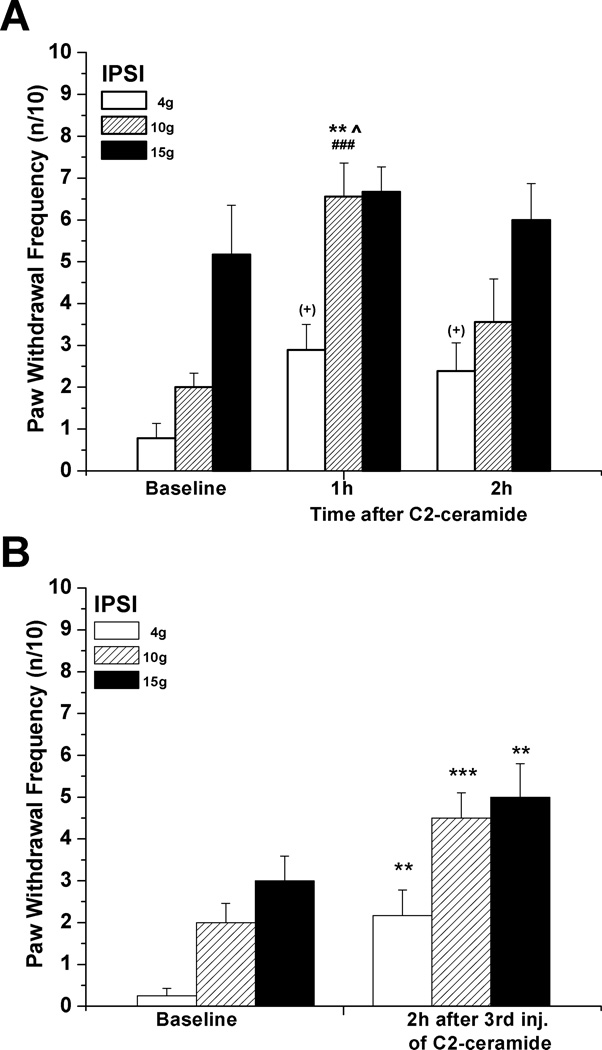
Figure 2.
Mechanical hyperalgesia induced by local C2-ceramide. (A) C2-ceramide (20 µg/10 µL) injected s.c. into the rat plantar hind paw caused an acute increase in responsiveness to stimulation with low and medium forces (4g, 10g) (n=9). **P<0.01 vs. baseline, ^P<0.05 vs. responses at 2h (Friedman test followed by Dunn's post hoc test), ###P<0.005 compared to the contralateral values (two-tailed Mann-Whitney test); for allodynia: (+) p=0.0450 (Friedman test), without significant difference between rank sum means (Dunn's post hoc test). (B) In comparison, significantly elevated ipsilateral responsiveness to stimulation by all 3 forces was observed at 2h after the 3rd of 3 consecutive s.c. injections of C2-ceramide (20 µg/10 µl) given every 75min into the same plantar spot (n=12). **P< 0.01, **P< 0.005 (Wilcoxon matched pairs test, two-tailed).