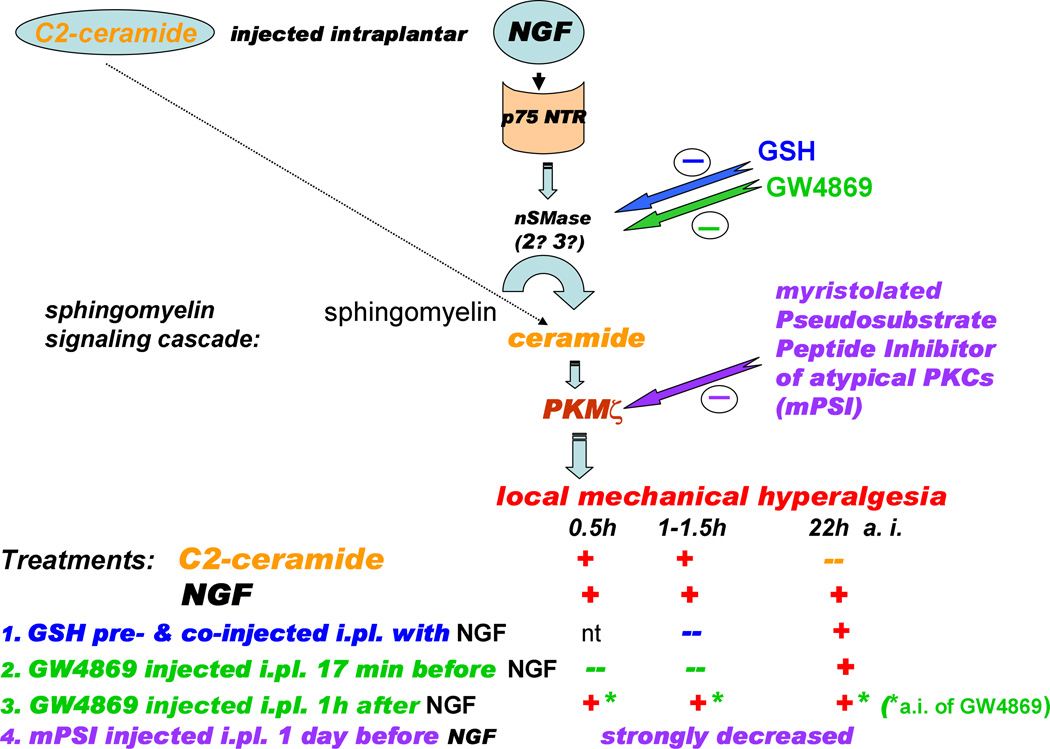
Figure 8.
The intracellular signaling pathway downstream of p75NTR which leads to mechanical hyperalgesia from NGF in rat plantar hind paw, and a summary of the antihyperalgesic effects of the treatments used in the current work. NGF induced a long-lasting hyperalgesia (up to 24h), while the effect from a single injection of C2-ceramide was brief (<2h). Both inhibitors of nSMase, GSH (at a high total dose) and GW4869, prevented the acute hyperalgesia from NGF. A post facto application of GW4869, however, failed to reverse NGF-induced hyperalgesia. Intraplantar pre-treatment with myristoylated pseudosubstrate inhibitor of aPKCs, mPSI, (1 day before) strongly decreased the hyperalgesic actions of NGF. Key: (+) - hyperalgesia was observed; (--) - hyperalgesia was not observed; nt – not tested.