Figure 3. Anti-allodynic effects of i.t. deltorphin II in CFA rats.
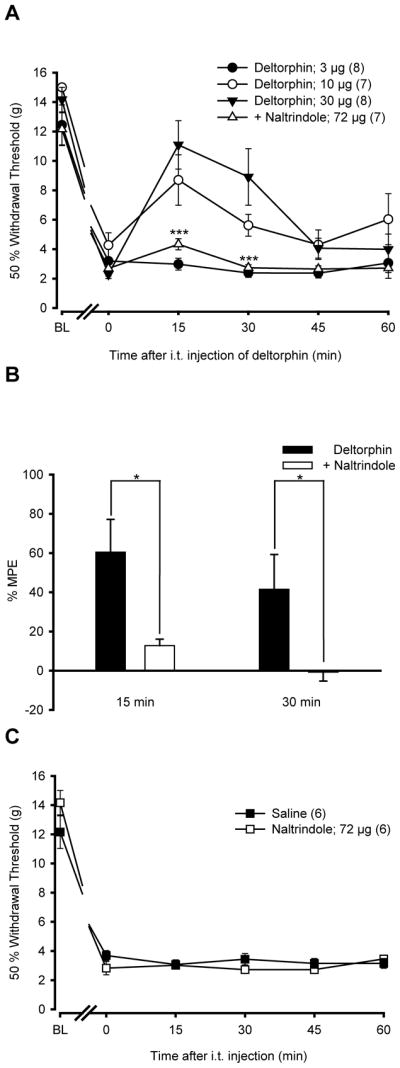
(A) Rats were injected with CFA in the plantar surface of the left hind paw. Six days after CFA injection, the 50% paw withdrawal threshold (in g) was measured using von Frey hairs every 15 min over a period of 60 min following i.t. injection of deltorphin II (Delt II; 3, 10, 30 μg) alone or following naltrindole (NTI; 72 μg) injection. BL indicates the baseline for 50% withdrawal threshold just before CFA injection, and time 0 indicates the paw withdrawal threshold immediately before deltorphin II injection. Intrathecally-administered deltorphin II induced a dose-dependent (3, 10, 30 μg) reduction of mechanical allodynia of the ipsilateral hind paw of CFA-treated rats (FTreatment=15.83 with P<0.0001, two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test). The anti-allodynia induced by deltorphin II peaked 15 min after the injection. Intrathecally-administered naltrindole, 10 min prior to deltorphin II injection (a 3:1 molar ratio of NTI/Delt II = 72/30 μg), reversed the anti-allodynia induced by deltorphin II at 15 min post-injection (FTreatment=25.53 with P<0.0001, two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test). (B) The %MPE ± S.E.M. was determined 15 and 30 min after injection of deltorphin II alone or in combination with NTI. The %MPE for deltorphin II injected after NTI was lower than the %MPE of deltorphin II-injected rats, indicating that the effect of deltorphin II was DOPR-mediated (* P<0.05 at 30 min, two-tailed unpaired t-test). (C) As compared with saline, by itself i.t. NTI (72 μg) has no effect on the CFA-induced mechanical allodynia (FTreatment=3.13 with P>0.05, two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test).
