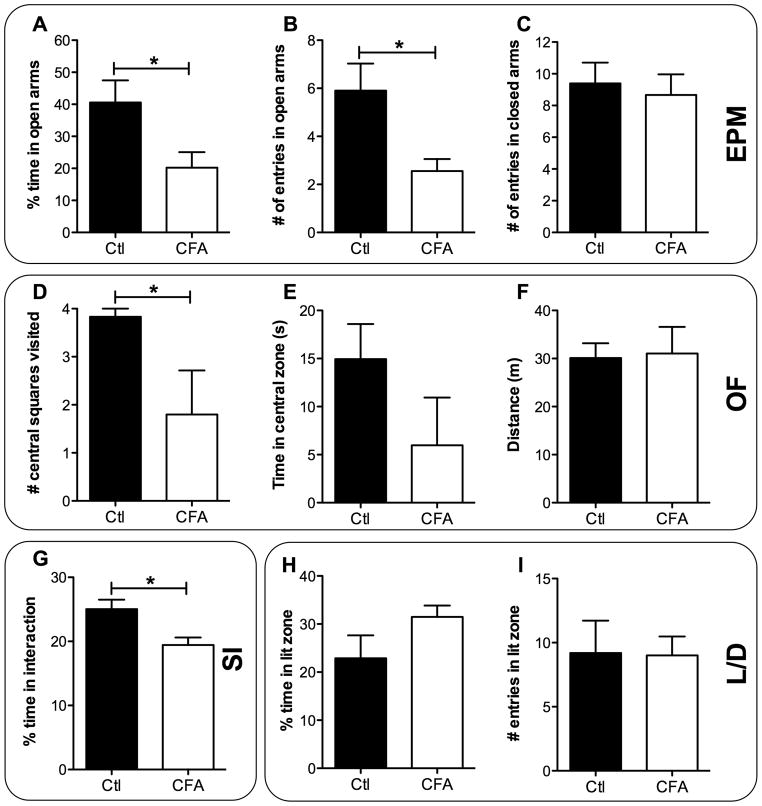
FIGURE 2. Development of anxiety-like behaviors caused by chronic inflammatory pain.
Anxiety-like behaviors were measured on CFA- and saline-treated (control) animals using the elevated-plus maze (EPM), open field (OF), social interaction (SI) and light/dark exploration (L/D) tests. (A) Percentage of time spent in open arms, (B) number of entries in open arms and (C) number of entries in closed arms measured in the EPM on day 29 (n = 9–10 in both CFA and control groups). (D) Number of virtual central squares visited (on a total of 4), (E) time in the central zone and (F) total distance travelled were measured in the OF test on day 30 (n = 5–6 in each group). (G) Percentage of time focal animals spent actively interacting with social animals measured in the SI test on day 28 (n = 9 in the control group and n = 25 in the CFA group). (H) Percentage of time spent and (I) number of entries in the lit zone measured in the L/D test on day 29 (n = 5 in both CFA and control groups). All data represent means ± S.E.M. Statistical analyses were performed using the parametric unpaired t-test. The asterisks denote significant differences from saline-injected animals; *P < 0.05.