Figure 2.
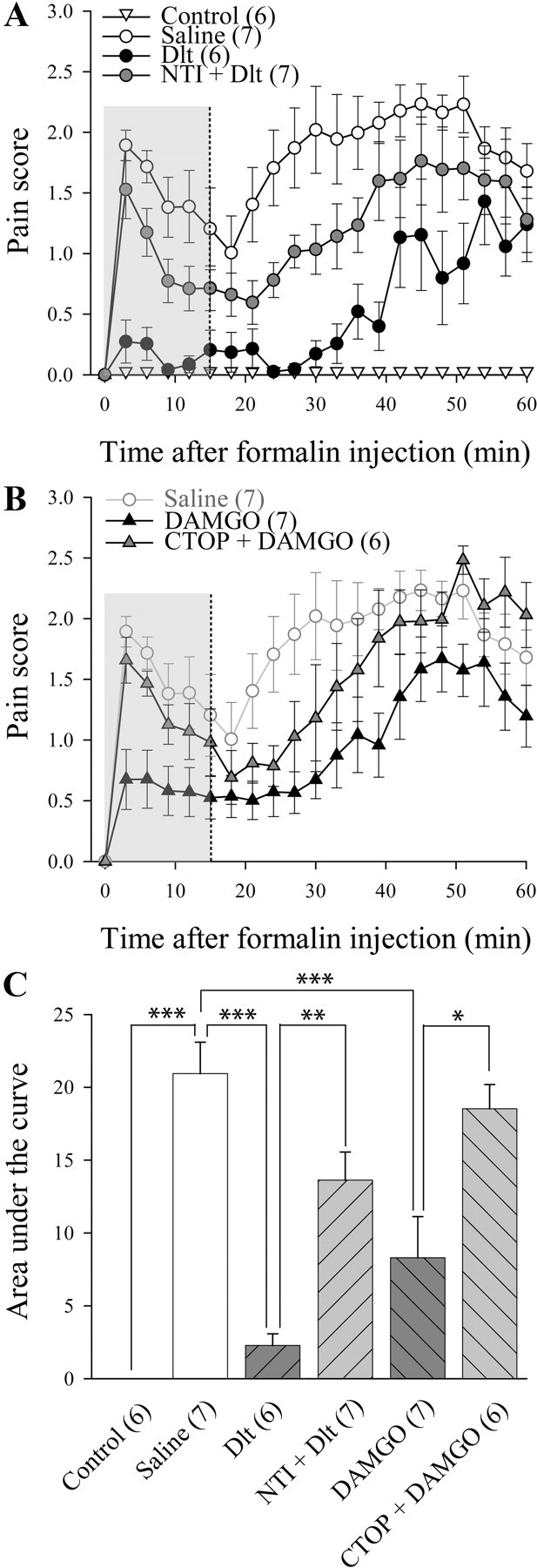
Inhibition of formalin-induced pain behavior following activation of DOPR and MOPR. Sprague Dawley male rats were injected with intradermal formalin (50 μl of 5.4%) in the plantar surface of the hindpaw, and pain behaviors were recorded during 60 min. A, Unlike intraplantar injection of saline, intraplantar injection of formalin produced a biphasic nociceptive response. Intrathecally administered deltorphin II (10 μg; 12.7 nmol) produced a decrease in formalin-induced pain behaviors. NTI (50 nmol) reversed the effects of Dlt II. B, Intrathecally administered DAMGO (1 μg; 1.9 nmol) produced a decrease in formalin-induced pain behaviors compared with saline (for reference purpose, results presented are the same as in A). CTOP coinjection (6 nmol) reversed the effects of DAMGO. C, Graphic representation of AUC for the first 15 min (highlighted by a gray area in A and B) was calculated from data presented in A and B. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post hoc test. The numbers in parentheses represent the number of animals per group. Error bars indicate SEM.
