Figure 3.
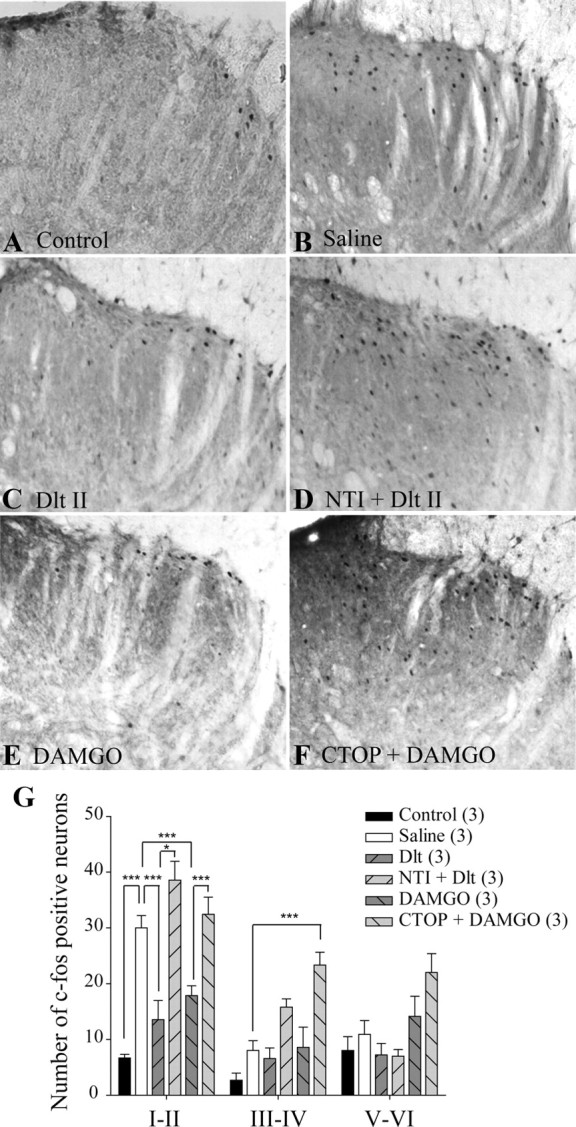
Reduction of formalin-induced neuronal activation by DOPR and MOPR agonists. Sprague Dawley male rats were injected with intradermal formalin (50 μl of 5.4%) in the plantar surface of the hindpaw, and c-fos expression in the spinal cord was observed by immunohistochemistry. When intradermal vehicle was injected, little c-fos expression was observed (A), whereas formalin induced robust c-fos expression (B). C, Rats treated with intrathecal Dlt II (10 μg; 12.7 nmol) 5 min before formalin displayed a significant reduction in c-fos expression. D, NTI (50 nmol) reversed the effects of Dlt II. E, Intrathecal DAMGO (1 μg; 1.9 nmol) also produced a reduction in c-fos expression, and this effect was suppressed by CTOP (6 nmol) (F). CTOP also induced an increase in c-fos expression in deeper laminae (F). G, Graphic representation of the number of c-fos-positive neurons. *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post hoc test. The numbers in parentheses represent the number of animals per group. Error bars indicate SEM.
