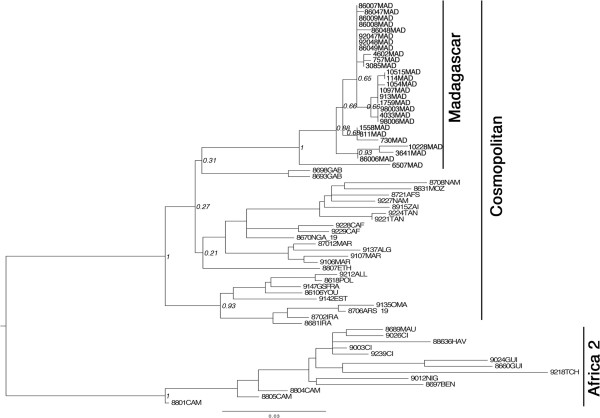
Figure 4.
Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree of 66 partial N gene sequences (Positions 127–629 nucleotides of the rabies virus genome [[30]]) showing phylogenetic relationships of Malagasy isolates with other isolates originating from Africa. The phylogenetic trees was estimated using a maximum-likelihood (ML) method under the general time-reversible (GTR) model of nucleotide substitution, with the rate of each substitution type estimated from the data using PHYML 3.0 [31]. The ML base frequencies were also estimated from the data, as were the proportion of invariable sites (I) and a gamma distribution of rate variation among sites (Γ) with four rate categories. Tree topology was estimated using the best estimates among simultaneous Nearest Neighbour Interchanges and the approach relying on subtree pruning and regrafting. The support of the data for each internal branch of the phylogeny was estimated using non-parametric bootstrap. Bootstrap support of nodes discussed in the text is indicated. The tree is rooted between the Africa 2 and the Cosmopolitan lineages. The generated sequences have been deposited in GenBank under accession numbers KC787050 to KC787074, DQ420623 and U22854.