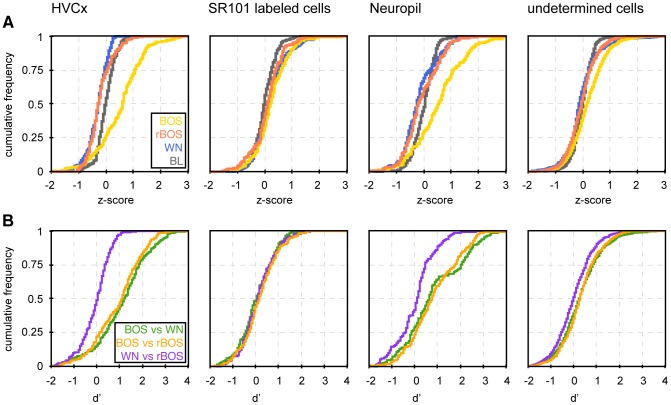
Figure 5. Auditory responses display preference for BOS in HVCX neurons but not in astroglia.
A Cumulative distributions of Z-scores in different ROI types and for different auditory stimuli. HVCX neurons are strongly excited by BOS (yellow) but weakly inhibited by WN (blue) and rBOS (red). A very similar finding applies to neuropil, but not to astroglia in which auditory stimulation only elicits weak responses. The Z-score cumulative distributions during baseline periods (black) are antisymmetric and centered around zero, they depict the range of Z-scores associated with baseline signal fluctuations. B Distribution of d′ values in different ROI types and stimulus pairs. HVCX neurons clearly prefer BOS over rBOS (orange, median d′ = 1.13) and BOS over WN (green, median d′ = 1.25), but display no differential responses to WN vs. rBOS (purple, median d′ = 0.05). A similar behavior is seen in neuropil, though there the preferences for BOS over rBOS (median d′ = 0.76) and BOS over WN (median d′ = 0.67) are less pronounced than in HVCX neurons. Astrocytes slightly prefer BOS over rBOS (median d′ = 0.18) but even less pronounced is their preference for BOS over WN (median d′ = 0.06).