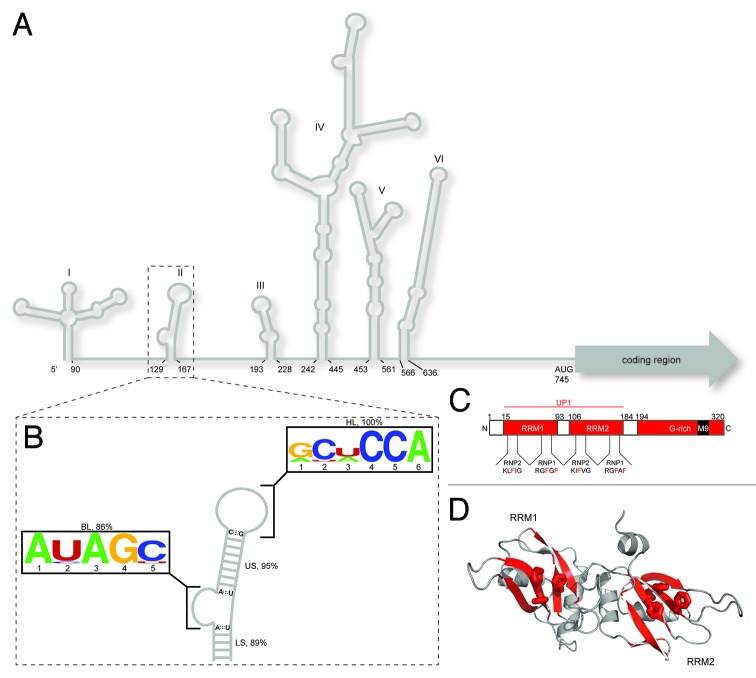
Figure 1. Overview of cis and trans acting factors that affect EV71 RNA translation. (A) Schematic representation of the RNA secondary structure of the EV71 5′ NCR. Stem loop I functions in negative strand synthesis, whereas stem loops II‒VI comprise the type I IRES element. (B) Consensus secondary structure of the SLII domain derived from sequence alignments (n = 147; see SI for accession codes) coupled with RNA structure prediction. SLII can be divided into four conserved elements of secondary structure: a five bp lower stem (LS, 89%); a five nt bulge loop (BL, 86%); a nine bp upper stem (US, 95%) and a six nt hairpin loop (HP, 100%), where percent values correspond to conservation of secondary structural elements not sequence. The BL and HL closing base pairs are invariably AU and CG, respectively. Consensus sequence motifs for the bulge and hairpin loops are depicted using the WebLogo format.55 (C) Domain organization of hnRNP A1 showing the N-terminal RNA recognition motifs (collectively known as UP1) and the C-terminal glycine rich domain. Signature RNP motifs are designated for RRM1 and RRM2 (D) Cartoon representation of the UP1 structure (PDB 2LYV) where aromatic residues from RNP1 and 2 are drawn as sticks.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.