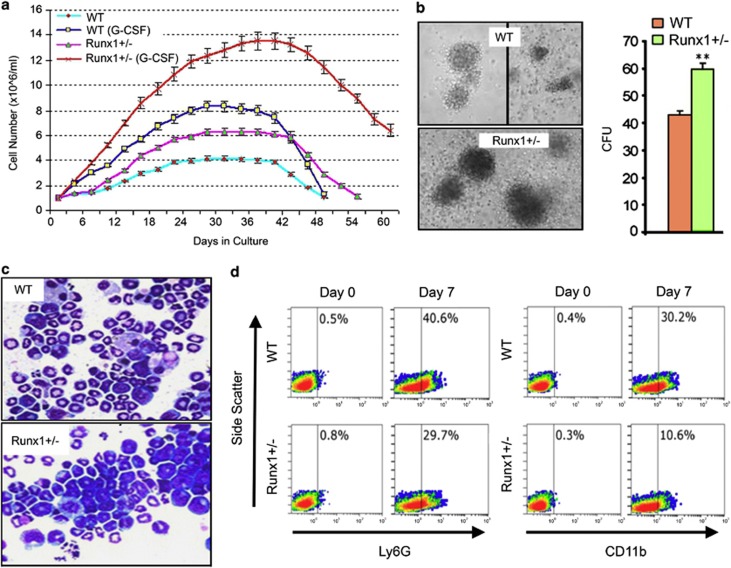
Figure 1.
Runx1-haploinsufficient cells are able to lineage commit but have impaired subsequent maturation. Lineage-negative (Lin−) cells were isolated from bone marrow of Runx1+/− (haploinsufficient) and wild-type (WT) C57BL/6 mice using MACS Lineage Cell Depletion Kit (#130-090-858, Miltenyi Biotec Inc., Auburn, CA, USA). (a) Cell counts. Cytokine supplementation: 10 ng/ml of mSCF and 100 ng/ml of thrombopoietin (non-differentiation promoting conditions) or 10 ng/ml of murine stem cell factor, 10 ng/ml of mIL-6 and G-CSF 20 ng/ml (PeproTech Inc., Rocky Hill, NJ, USA). Cell numbers were determined by automated cell counter every 3 days during 60 days of culture. Mean±standard deviation. Experiments performed in triplicate. (b) Colony formation by Runx1+/− and WT Lin− cells in semi-solid media. 2 × 104cells/ml of methylcellulose (MethoCult GF M3434; Stem Cell Technologies, Vancouver, Canada). Colonies counted and imaged by inverted microscope on day 10 (LeicaDMI6000B inverted microscope, Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany). Experiments performed in triplicate. ** p<0.01, Wilcoxon test. (c) Runx1+/− and WT cell morphology after 15 days of culture with G-CSF. Cytospins were generated with a Shandon CytoSpinIII (Thermo Scientific, Pittsburgh, PA, USA; 500 r.p.m., 5 min). Air-dryed cells fixed with 100% methanol were Giemsa-stained for visualization using a Leica DMR light microscope equipped with CCD camera (Leica Microsystems), magnification × 630. (d) Ly6G and CD11b granulocyte-lineage marker expression in Runx1+/− and WT Lin− cells on day 0 (D0) and day 7 (D7) of culture with G-CSF. Expression measured by Coulter Epics XL-MCL flow cytometer and CXP software (Beckman-Coulter, Brea, CA, USA). Antibodies used were anti-mouse Ly6G-FITC (eBiosciences, San Diego, CA, USA; #551460), anti-mouse CD11b-PE (eBiosciences, #120112), and isotype-matched immunoglobulin control.