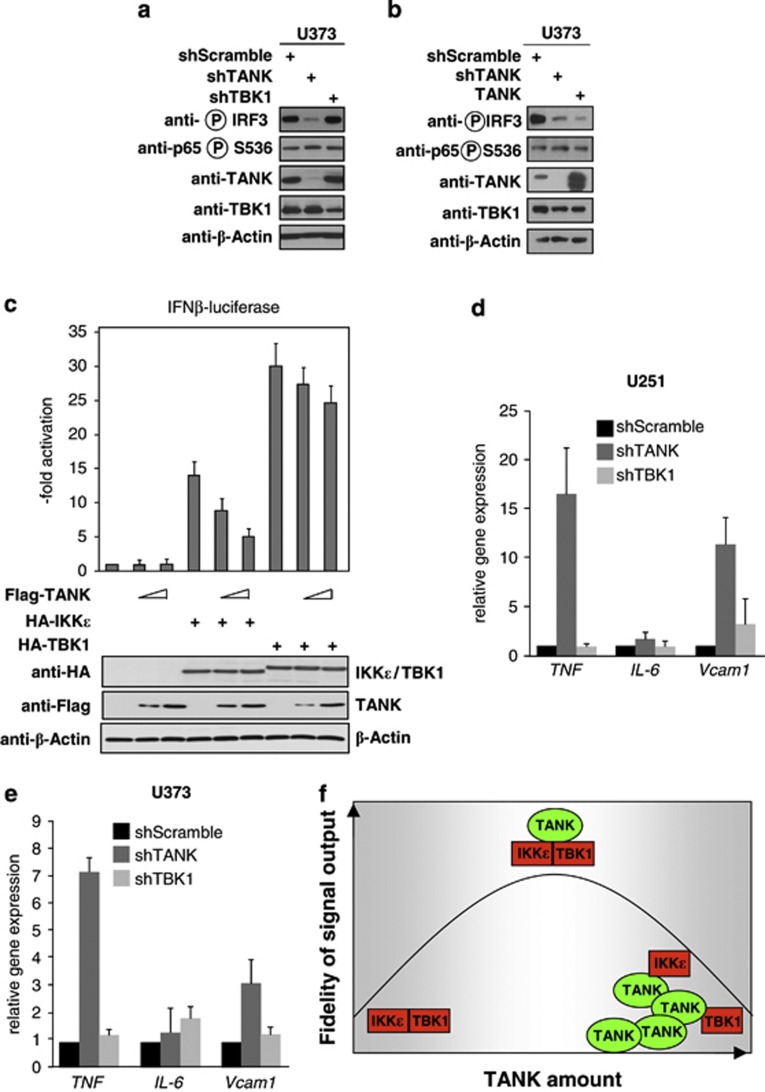
Figure 7.
Functional consequences of deregulated TANK expression. (a) TANK or TBK1 were knocked down in U373 cells with specific short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs), followed by the analysis of NF-κB p65 and IRF3 phosphorylation with specific antibodies. (b) TANK was overexpressed in U373 cells and extracts were analyzed for NF-κB p65 and IRF3 phosphorylation by western blotting. (c) HEK293 cells were transfected with a plasmid encoding the luciferase gene under the control of the interferon β (IFNβ) promoter along with the indicated expression vectors. After 36 h, cells were lysed and one aliquot was used for the determination of luciferase activity (upper) and the other aliquot was used to determine adequate protein expression. Error bars were derived from two experiments performed in triplicate. (d and e) TANK or TBK1 were knocked down in U373 (d) or U251 (e) cells, followed by quantitative analysis of proinflammatory gene expression by quantitative PCR (qPCR). (f) Schematic model illustrating that the fidelity of signal output is critically determined by the amount of TANK and the stoichiometric assembly of functional signaling complexes.