Figure 11.
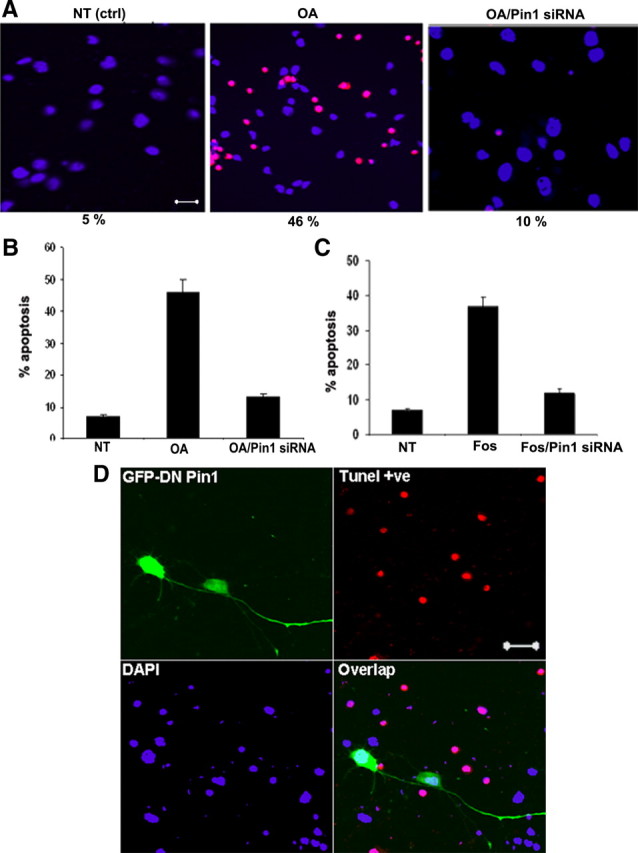
Inhibition of Pin1 reduces OA/Fos-induced neuronal death. A, Presence of apoptotic neurons examined by TUNEL–tetramethylrhodamine red staining in 7 DIC cortical neurons. Nuclei were counterstained using DAPI (blue). TUNEL-positive neurons were increased during OA treatment for 5 h and declined in OA-treated neurons transfected with Pin1 siRNA. Scale bar, 20 μm. The quantization in the bar graph (B) represents TUNEL-positive counts from four separate experiments, in which 12 independent fields were counted. NT (ctrl), Nontreated controls. B, The neuronal death is increased by 48% during exposure to OA (basal level, 5%), and this was reduced to 10% in neurons transfected with Pin1 siRNA and subjected to OA. C, The neuronal death is increased by 35% during exposure to Fos, and this was reduced to 12% in neurons transfected with Pin1 siRNA and subjected to Fos. D, OA-mediated neuronal apoptosis is reduced by overexpression of DN Pin1. Five-day-old cortical neurons were transfected with DN Pin1 and, after 24 h, were treated with 0.1 μm OA for 5 h. The GFP–DN Pin1-transfected neurons survive OA-induced cell death. Scale bar, 20 μm.
