Figure 5.
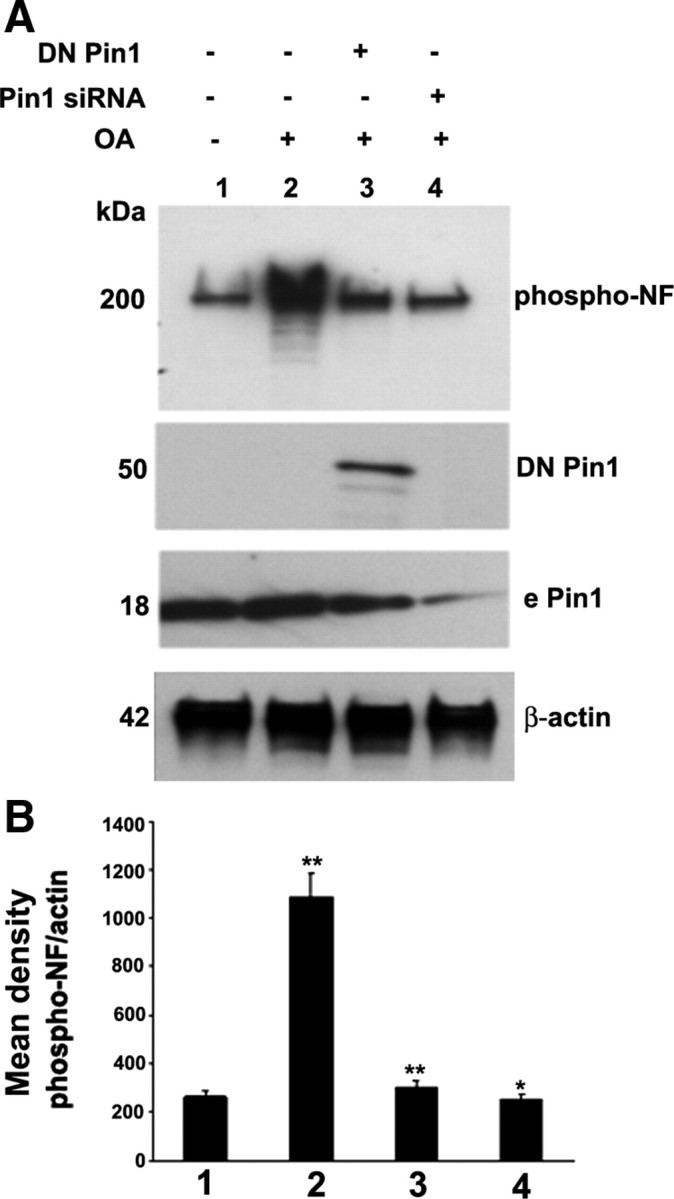
Pin1 expression and activity is critical toward OA-induced aberrant hyperphosphorylation of NF. A, Cortical neurons were subjected to treatment with OA (0.2 μm for 2.5 h), and Western blot analysis was performed with phospho-NF-M/H (SMI31) staining. The OA-induced hyperphosphorylation of NF is inhibited by knockdown of Pin1 by Pin1 siRNA and DN Pin1-transfected neurons. Lanes 1 and 2, Control scrambled siRNA-transfected neurons. Lanes 2–4, OA-treated neurons. Lane 3, Pin1 siRNA-transfected neurons. Lane 4, DN Pin1-transfected neurons. The transfected Pin1 is a GFP fusion protein and migrates at 50 kDa, at which the endogenous Pin1 (e Pin1) is 18 kDa. B, Densitometry analysis of phospho-NF immunoreactivity obtained from A. Mean density, Phospho-NF/actin is plotted on the y-axis. *p < 0.01 and **p < 0.001 of phospho-NF-M/H relative to nontreated neurons.
