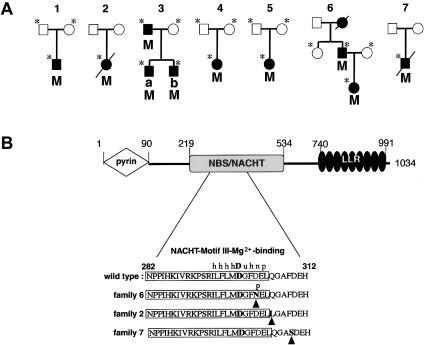
Figure 2.
A, Mutation segregation in pedigrees of families with CINCA. Square symbols denote males; circles denote females; affected individuals are denoted by blackened symbols, and segregating CIAS1 mutations are denoted by the capital letter M. In each pedigree, family members from whom DNA samples were available for analysis are marked by an asterisk. Autosomal dominant inheritance of CINCA is suggested by the segregation observed in families 3 and 6. B, Mutation locations on CIAS1 in three patients and domain structure of CIAS1. Residues 1–90 form the N-terminal pyrin domain, residues 219–534 form the NBS/NACHT domain, and residues 740–991 form the C-terminal leucine rich repeats. Shown at the bottom is the sequence of the NBS domain around the consensus motif-III Mg2+-binding site (boxed) found in the NACHT subfamily of NTPases (following Koonin and Aravind 2000) with the mutations (arrowheads) found in three families with CINCA. h = hydrophobic residues; u = tiny residues; n = negatively charged residues; p = polar residues.