Figure 6.
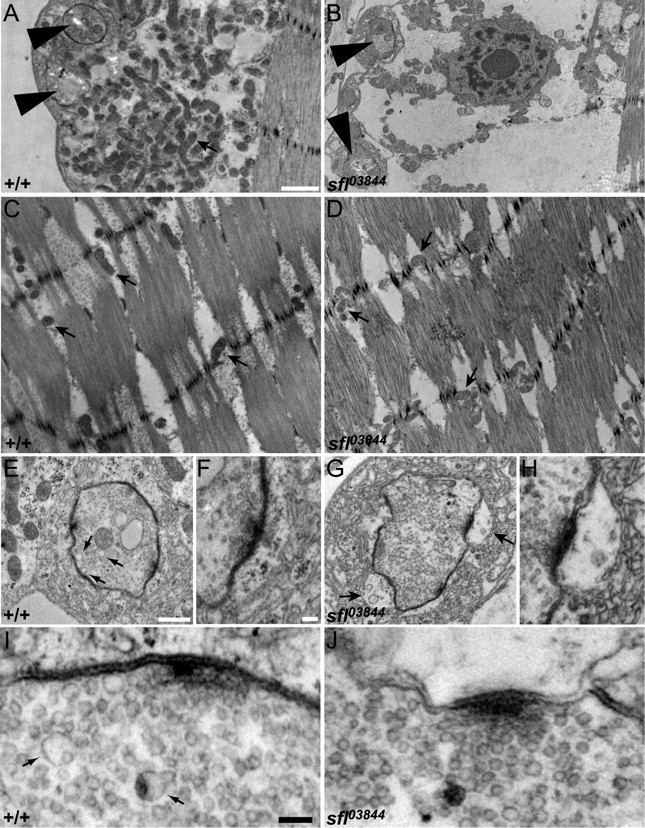
Ultrastructure of sfl mutant synapses. A, B, Electron micrographs showing synaptic boutons (large arrowheads) and the underlying muscle in wild-type and sfl03844 mutant NMJs. Wild-type NMJs have an abundance of mitochondria (arrow) between the boutons and the contractile fibers of the muscle, but sfl mutants have significantly fewer. Scale bar, 1 μm. C, D, Electron micrographs showing the contractile muscle fibers from wild-type and sfl mutant animals (same scale as in A and B). Similar numbers of mitochondria (arrows) are found within the contractile apparatus of sfl mutant muscles as in wild type. E–H, Higher-magnification views of boutons from wild-type and sfl mutant animals. Scale bars: E, G, 0.5 μm; F, H, 0.1 μm. The arrows in E point to 70 nm cisternae, which are more numerous in wild type than in sfl mutants. The arrows in G point to enlarged pockets between the postsynaptic membrane and the subsynaptic reticulum in sfl mutants. I, J, Electron micrographs showing synaptic vesicles near active zones in wild type and sfl mutant NMJs. Scale bar, 0.1 μm. Numerous 35 nm vesicles are seen in both genotypes, but sfl mutants have fewer 70 nm cisternae (arrows) than controls.
