Figure 1.
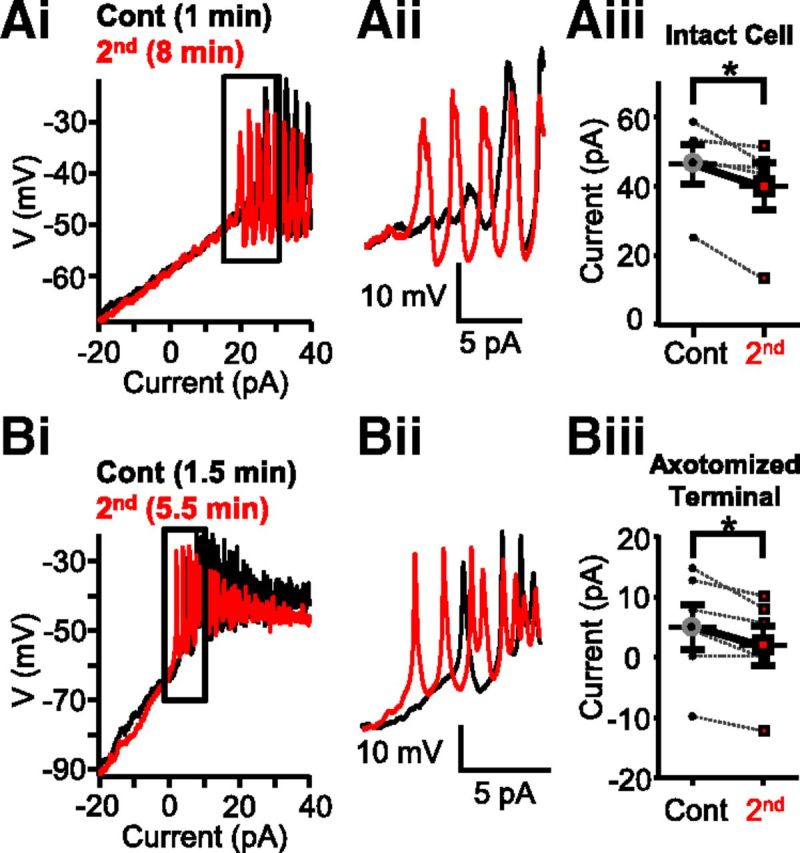
Strong depolarization shifted calcium spike threshold in Mb-type bipolar cells. Ai, Consecutive current ramp recordings made directly from the large axon terminals of intact Mbs in goldfish retinal slice preparation. Less depolarizing current was needed to evoke spikes when a second current ramp was applied 8 min (red) after the first (black). Aii, Enlargement of Ai focusing on the region of spike initiation. The initiation of spikes is shifted leftward for the 8 min trace. Aiii, Summary showing less current required for the initiation of Ca2+ spikes in terminals of whole Mbs in response to current ramp when preceded by strong depolarization. Data are taken from leak-subtracted and normalized traces. *p = 0.03 (paired Student's t test). n = 5. Bi, Current ramp evoked Ca2+ spikes recorded from an axotomized Mb terminal in slice preparation. The second current ramp (red represents 5.5 min after break-in) triggered spikes with less depolarizing current than the first current ramp (black represents 1.5 min after break-in). Bii, Enlargement of the regions of spike initiation from Bi. There is a leftward shift in the red trace. Biii, Summary showing that less current is required for the initiation of Ca2+ spikes in axotomized Mb terminals in response to current ramp when preceded by strong depolarization. Data are taken from leak-subtracted and normalized traces. *p = 0.02 (paired Student's t test). n = 5. Data are mean ± SEM.
