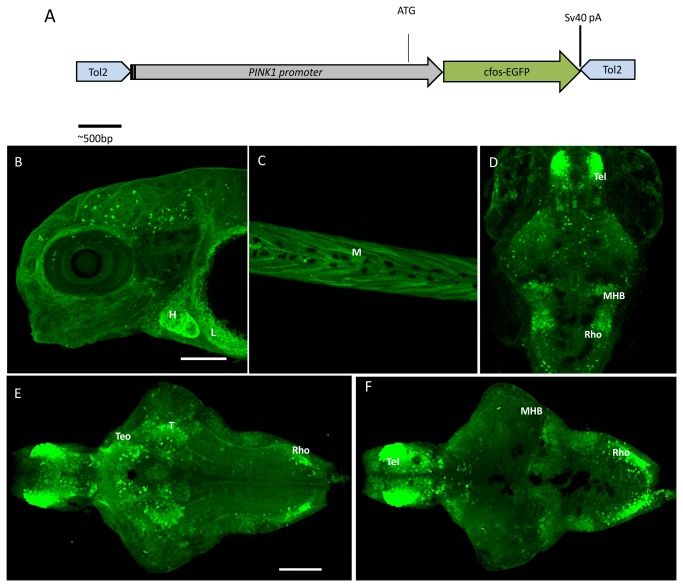
Figure 1. The PINK1 promoter construct and expression pattern in zebrafish larva of the Tg(pink1:EGFP) line.
A. Construction of the PINK1 promoter DNA fragment comprising the sequence -2 kb upstream of the 5’ end of the pink1 gene and including the ATG start site. This is inserted in the cloning site in the Tol2 transposon vector pCS-cfosGFP, which contains a small intronic sequence and a GFP expression cassette having minimal cfos activity [21]. B-F. Confocal z-stack images of the whole-mount Tg(pink1:EGFP) larval stages.
B. GFP expression as observed in peripheral tissues at different stages of development by GFP IHC. In a lateral view of 4 dpf whole mount larvae, expression was observed in the heart (H) and liver (L); anterior to the left.
C. Expression in the muscle of the 4-dpf larvae in a lateral view (M); anterior to the left.
D. The whole mount GFP expression at 5 dpf; dorsal views, anterior to the top, showing pronounced immunoreactive cells in brain regions such as the telencephalon (Tel), mid-hindbrain boundary (MHB) and rhombencephalon (rho).
E- F. Dorsal and ventral views of the brain of 7-dpf Tg(pink1:EGFP) fish; anterior to the right.
E. In the ventral view, the strongest GFP expression is seen in the telencephalon (Tel), anterior part of optic tectum (TeO), thalamus (T), and the lateral rhombencephalon (rho). F. The dorsal view shows the prominent expression in the mid-hindbrain boundary (MHB) along with Tel and rho.
Scale bar represents 100μm. GFP – Green fluorescent protein, PINK1 – PTEN-induced putative kinase 1.