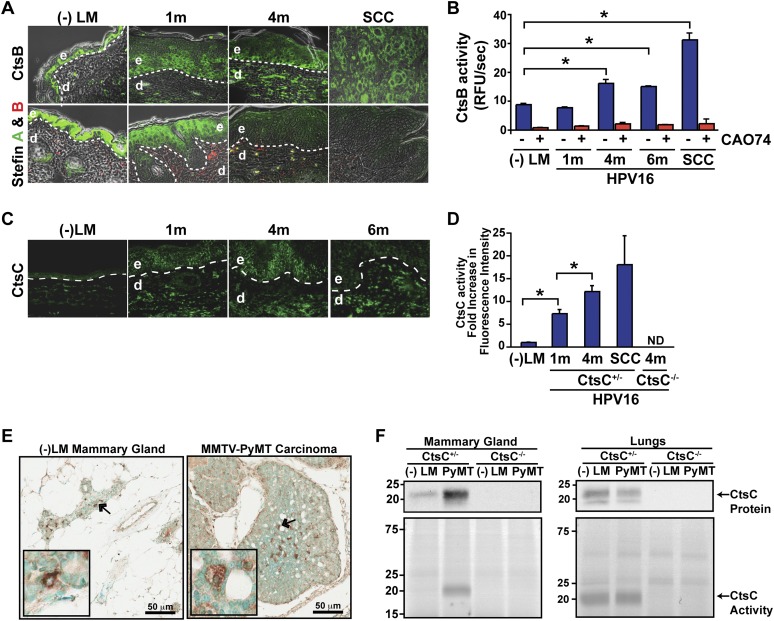
Figure 1.
Increased CtsB and CtsC expression and activity during cancer development. (A, top panels) Localization of CtsB expression in skin of congenic negative littermates (−LM), premalignant skin of HPV16 mice at 1 and 4 mo of age, and SCCs as assessed by immunofluorescence staining. (Bottom panels) CtsB endogenous inhibitors, Stefin A, and Stefin B expression in skin of negative littermates (−LM), premalignant skin of HPV16 mice at 1 and 4 mo of age, and SCC tissue. (B) Enzymatic activity of CtsB in whole-tissue lysate as determined by incubation with the fluorogenic substrate Z-Phe-Arg-AMC.HCl. (AMC) 7-Amino-4-methyl coumarin. CtsB-selective inhibitor CA074 was added to tissue lysates as a control (red bars). n ≥ 3 mice per group. (C) Immunofluorescent detection of CtsC in negative littermate (−LM) ear skin and hyperplastic (1m), early dysplastic (4m), and late dysplastic (6m) ear tissue of HPV16 mice. (D) Quantitation of FY01 labeling of enzymatically active CtsC within total cell extracts derived from HPV16 ear tissue. n = 3 mice per group. (E) Immunodetection of CtsC in representative mammary gland and tumor tissue from CtsC-proficient animals. Arrows mark the areas displayed in the insets. (F, bottom panels) FY01 labeling of active CtsC within total cell extracts from nontransgenic mammary glands (−LM), mammary tumors (PyMT), and normal (−LM) and metastatic (PyMT) lungs. (Top panels) CtsC protein levels were assessed by Western blotting, and CtsC-proficient (CtsC+/−) and CtsC-deficient (CtsC−/−) samples are as indicated. Significance was determined by an unpaired t-test; (*) P < 0.05.