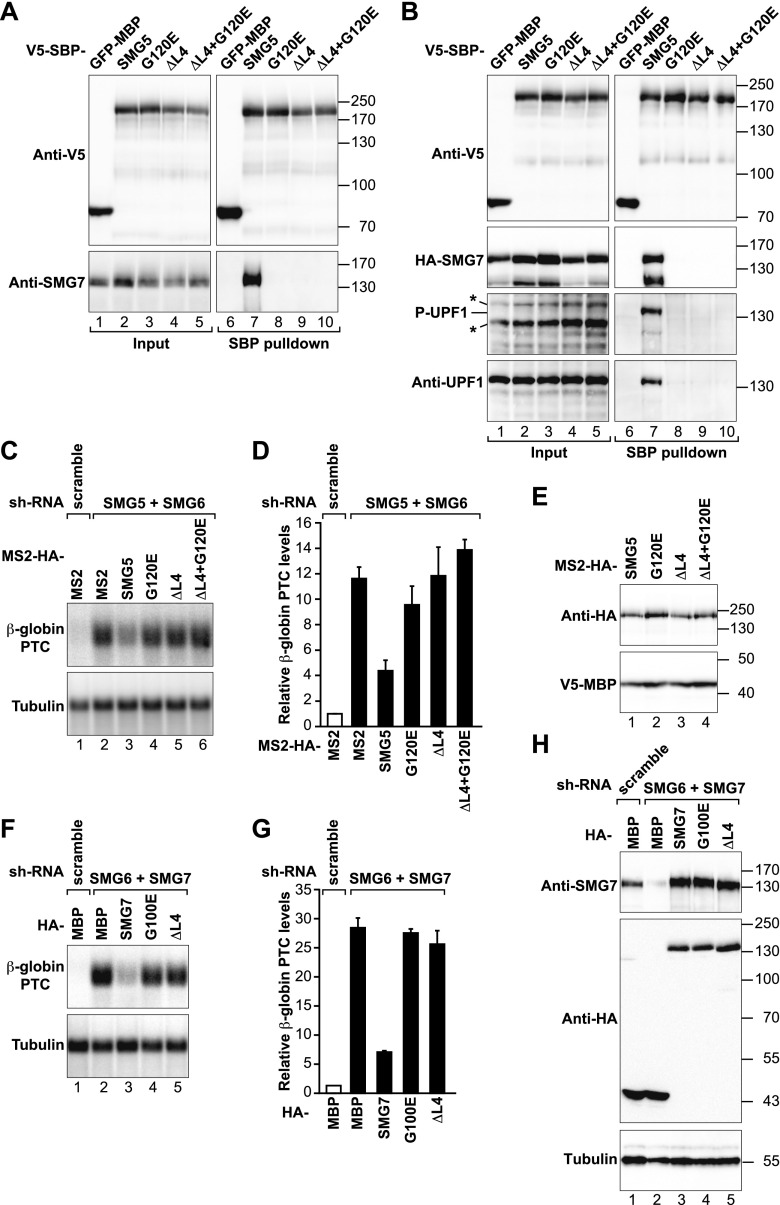
Figure 1.
SMG5–SMG7 heterodimerization is required for NMD. (A) Interaction of SMG5-V5-SBP-MBP (wild type or mutants) with endogenous SMG7 in HEK293T cells. A V5-SBP-tagged GFP-MBP fusion served as a negative control. Inputs (1%) and bound fractions (5%) were analyzed by Western blotting. Samples were treated with RNase A before the pull-down. (B) Interaction of SMG5-V5-SBP-MBP (wild type or mutants) with endogenous and phosphorylated UPF1 (P-UPF1) and HA-SMG7 in cell lysates treated with RNase A. Inputs (1%) and bound fractions (2% for the SBP and HA-tagged proteins and 30% for UPF1) were analyzed by Western blotting. Asterisks indicate phosphorylated proteins (distinct from UPF1) recognized by the phospho-(Ser/Thr) ATM/ATR substrate antibody in input samples. The identity of phosphorylated UPF1 in the pull-down was confirmed by reprobing the membrane using anti-UPF1 antibodies. (C–E) HeLa cell lines expressing the β-globin NMD reporter (containing a PTC) were transfected with plasmids expressing the indicated shRNAs. Plasmids expressing shRNA-resistant versions of MS2-HA-SMG5 (wild type or mutants) were included in the transfection mixtures as indicated. MS2-HA served as a negative control. (C) The levels of the PTC-containing β-globin reporter were analyzed by Northern blotting, normalized to those of endogenous β-tubulin mRNA, and set to 1 in control cells (i.e., cells expressing MS2-HA and treated with a scrambled shRNA). D shows mean values ± standard deviations obtained in three independent experiments. (E) Expression of MS2-HA-SMG5 (wild type or mutants) in the complementation assay. V5-SBP-MBP served as a transfection control. (F,G) A complementation assay as described in C and D was performed in cells codepleted of SMG7 and SMG6 and transfected with plasmids expressing shRNA-resistant HA-SMG7 (wild type or mutants). (H) Expression of HA-SMG7 (wild type or mutants) in the complementation assay shown in F and G.