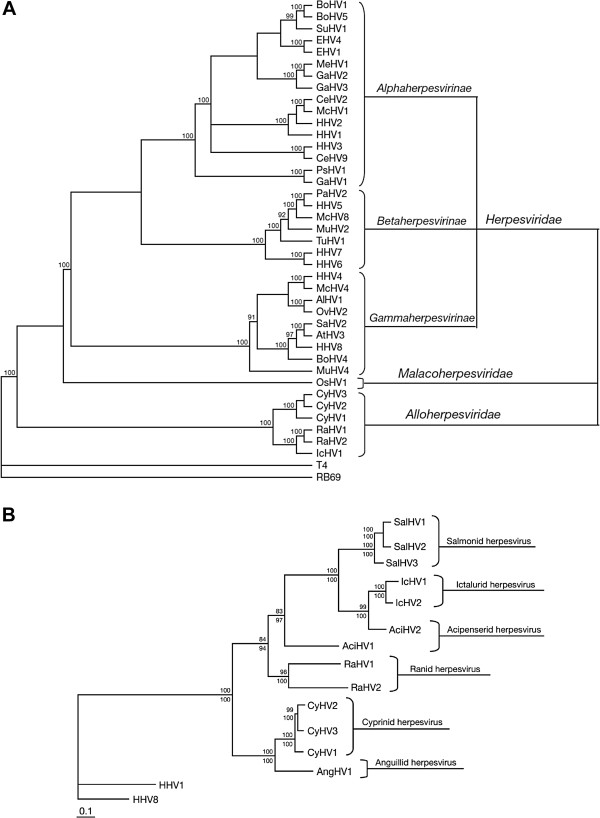
Figure 1.
Phylogeny of the order Herpesvirales and the Alloherpesviridae family. (A) Cladogram depicting relationships among viruses in the order Herpesvirales, based on the conserved regions of the terminase gene. The Bayesian maximum likelihood tree was rooted using bacteriophages T4 and RB69. Numbers at each node represent the posterior probabilities (values > 90 are shown) of the Bayesian analysis. (B) Phylogenetic tree depicting the evolution of fish and amphibian herpesviruses, based on sequences of the DNA polymerase and terminase genes. The maximum likelihood tree was rooted with two mammalian herpesviruses (HHV-1 and HHV-8). Maximum likelihood values (> 80 are shown) and Bayesian values (> 90 are shown) are indicated above and below each node, respectively. Branch lengths are based on the number of inferred substitutions, as indicated by the scale bar. AlHV-1: alcelaphine herpesvirus 1; AtHV-3: ateline herpesvirus 3; BoHV-1, -4, -5: bovine herpesvirus 1, 4, 5; CeHV-2, -9: cercopithecine herpesvirus 2, 9; CyHV-1, -2: cyprinid herpesvirus 1, 2; EHV-1, -4: equid herpesvirus 1, 4; GaHV-1, -2, -3: gallid herpesvirus 1, 2, 3; HHV-1, -2, -3, -4, -5, -6, -7, -8: human herpesvirus 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8; IcHV-1: ictalurid herpesvirus 1; McHV-1, -4, -8: macacine herpesvirus 1, 4, 8; MeHV-1: meleagrid herpesvirus 1; MuHV-2, -4: murid herpesvirus 2, 4; OsHV-1: ostreid herpesvirus 1; OvHV-2: ovine herpesvirus 2; PaHV-1: panine herpesvirus 1; PsHV-1: psittacid herpesvirus 1; RaHV-1, -2: ranid herpesvirus 1, 2; SaHV-2: saimiriine herpesvirus 2; SuHV-1: suid herpesvirus 1; TuHV-1: tupaiid herpesvirus 1. Reproduced with permission from Waltzek et al. [14].