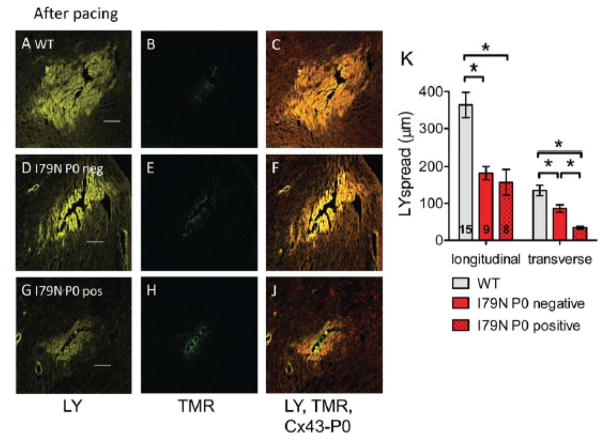
Fig. 7. Reduced gap junctional coupling assessed by modified scrape loading.
(A,D,G) Representative confocal images of Lucifer yellow (LY, yellow) spread after needle puncture in TnT hearts after pacing. (B,E,H) Corresponding images of non-gap junction permeable Tetramethylrhodamine dextran (TMR, green) that was simultaneously injected. (C, F, J) Composite image of LY, TMR and Cx43-P0 (red). The scale bar length is 100 μm. (K) Summary data of LY spread analysis from 15 sites in TnT-WT (3 hearts) and 17 sites in TnT-I79N hearts (4 hearts). For TnT-I79N only sites were analyzed that were clearly classified as Cx43-P0 negative (I79N P0 neg, n=9) or showed clear Cx43-P0 accumulation along at least two sides (I79N P0 pos, n=8). Dye spread was analyzed along the fiber (longitudinal) or across the fiber (transverse). * p≤0.05 vs. as indicated