Fig. 1. Change of CBF in tracheal rings from control and alcohol-drinking mice ± supplemental dietary antioxidants (NAC or procysteine).
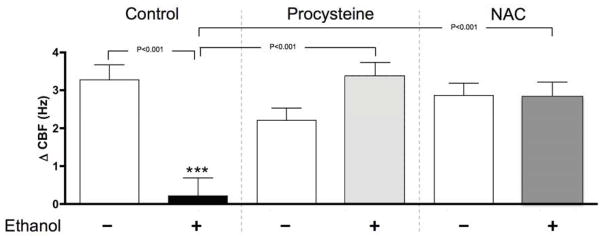
Change in ciliary beat frequency following procaterol (from baseline) is represented on the vertical axis in cycles/sec (Hz). A pre-activation baseline CBF measurement made for each group was subtracted from the procaterol-stimulated CBF responsiveness to calculate ΔCBF. Alcohol-only mice had significantly reduced CBF responsiveness compared to naïve mice. Alcohol-drinking mice fed dietary antioxidants of procysteine or NAC had significantly increased procaterol responsiveness compared to alcohol-only mice and were not significantly different from naïve mice.
