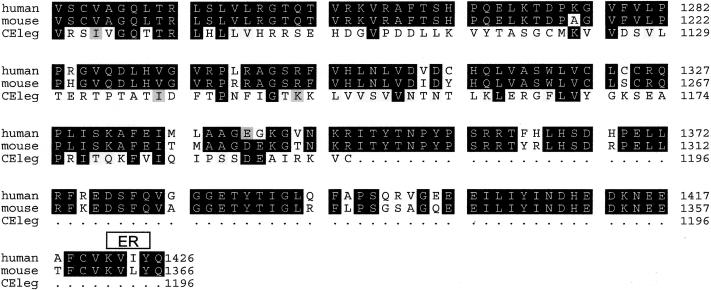
Figure B.
Alignment of human, mouse, and C. elegans deduced nephroretinin sequences. The order from top to bottom is human, mouse, and C. elegans (GenBank accession numbers BankIt 486643, BankIt 486675, and Z81579, respectively). Identities are shown in reverse (white on black), and similarities between all three sequences are shown on gray background. There was 82% amino acid identity between human and mouse sequences and 23% amino acid identity between human and C. elegans sequences. Boxes above the sequence delimit motifs as predicted by the programs given in parenthesis: NLS = nuclear localization domain (ACEVIEW); ER = endoplasmic reticulum membrane domain (ACEVIEW); E-rich = glutamic acid–rich domain (SMART); S-rich = serine-rich domain (SMART); P-rich = proline-rich domain (MOTIF SCAN); and DUF339 = PFAM (protein families database of alignments) domain of unknown function (MOTIF SCAN). In H. salinarium, the program BLAST detected a 30% sequence identity with gas-vesicle protein gvpL of H. salinarium (GenBank accession number P33964).