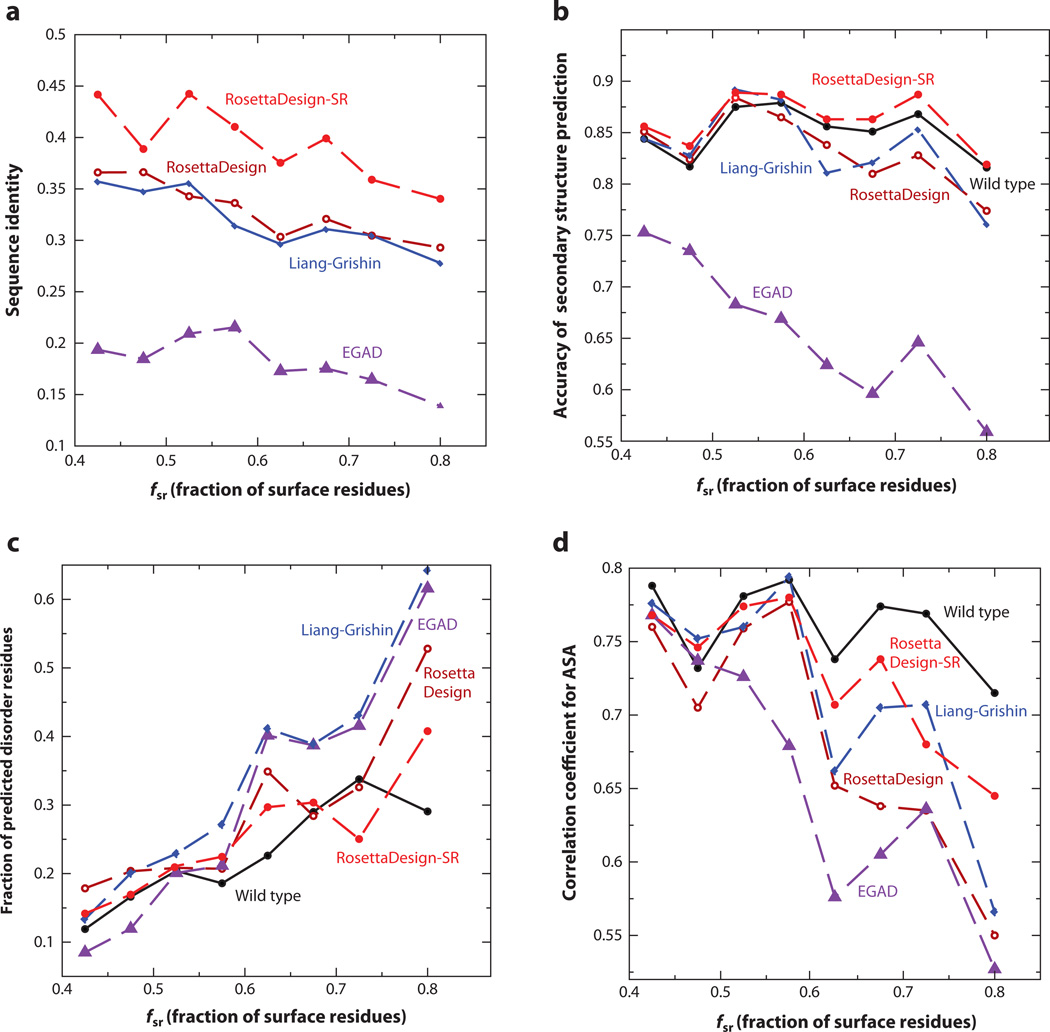
Figure 3.
(a) The average sequence identity of sequences designed by RosettaDesign-SR, RosettaDesign, Liang-Grishin, and EGAD is compared to their respective wild-type sequences as a function of the fraction of surface residues. (b) The average accuracy of predicted secondary structures from the sequences designed by four computational methods is compared with the results for wild-type sequences. SPINE-X was employed for sequence-based secondary structure prediction. (c) The average fractions of predicted disordered residues are compared. SPINE-D was employed for predicting intrinsic disorder for designed and wild-type sequences. (d) The average correlation coefficients between predicted and actual solvent-accessible surface areas (ASA) from the target structure are compared. Real-SPINE 3 was employed for solvent accessibility prediction from designed and wild-type sequences.