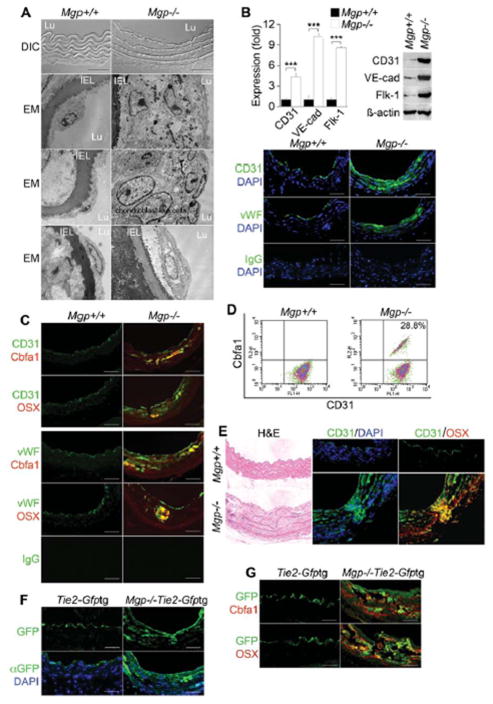
Figure 1. Endothelium contributes cells to aortic calcification of Mgp−/− mice.
(A) Aortic wall (confocal microscopy, top 2 panels), and aortic endothelium () from wild type (Mgp+/+) and Mgp−/− mice. DIC: differential interference contrast. EM: electron microscopy. Magnification for EM, 3.7 ×103. (B) Aortic expression of endothelial markers CD31, VE-cadherin (VE-cad), Flk-1 and vWF in Mgp+/+ and Mgp−/− mice determined by real-time PCR, immunoblotting and immunostaining. ***, p <0.001. (C) Immunostaining of aortic tissues from Mgp+/+ and Mgp−/− mice showed co-expression of endothelial markers CD31 (top) and vWF (bottom) and osteogenic markers Cbfa1 and Osterix (OSX) in the Mgp−/−mice. (D) Co-expression of CD31 and Cbfa1 in enzymatically dispersed CD45-negative aortic cells from Mgp+/+ and Mgp−/− mice, as determined by FACS. (E) Cells co-expressing CD31 and Osterix that have penetrated into the medial layer in Mgp−/− aorta. (F) Visualization of GFP (top) and immunostaining with anti-GFP antibodies (bottom) in aortic tissue of Tie2-Gfptg and Mgp−/−;Tie2-Gfptg mice. (G) Immunostaining of aortic tissues from Tie2-Gfptg and Mgp−/−;Tie2-Gfptg mice showed co-expression of GFP with Cbfa1 and OSX in the Mgp−/−;Tie2-Gfptg mice. Scale bars, 100 μm. DAPI (blue) was used to visualize nuclei. Non-specific IgG control showed no staining. Vessel lumen faces upwards in the photos unless otherwise indicated.