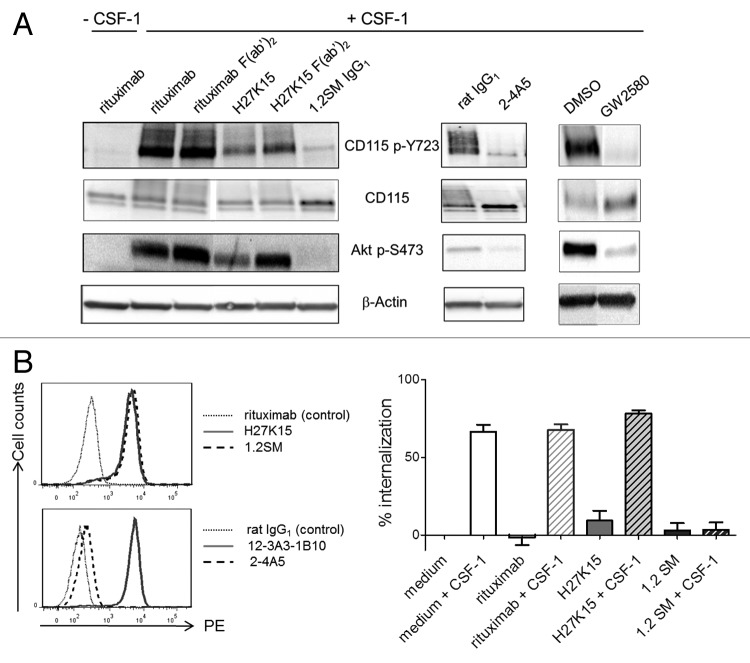
Figure 2. Effects of anti-CD115 mAbs on CSF-1-dependent signal transduction and receptor trafficking. (A) Effects on CD115-mediated signal transduction in AML5 cells. CSF1-deprived AML5 were treated with the indicated anti-CD115 mAbs, isotype controls, the TK inhibitor GW2580 or vehicle (DMSO) during 1h at 37°C. Cells were then stimulated for 3 min at 37°C with CSF-1 (100 ng/ml) and cell lysates were subjected to western blotting with anti-phospho-Tyr723 CD115, anti-CD115, anti-phospho-Ser473 Akt. Membranes were also probed with the anti-β actin antibody as a loading control. The results shown are representative from at least two independent experiments. (B) Effects on CSF-1-dependent CD115 internalization. Left panels: Immunostaining of EL4-CD115 cells with mAbs H27K15, 1.2SM or isotype control rituximab (top panel), or with mAbs 2–4A5, 12–3A3–1B10 or isotype control rat IgG1 (bottom panel). Right panel: CD115 internalization in EL4-CD115 cells stimulated or not with CSF-1 for 30 min in the presence or absence of mAbs. Remaining cell surface CD115 was measured by FC using detection mAb 12–3A3–1B10. Mean percentages of CD115 internalization +/− SD were calculated from 3 independent experiments as described in the Methods.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.