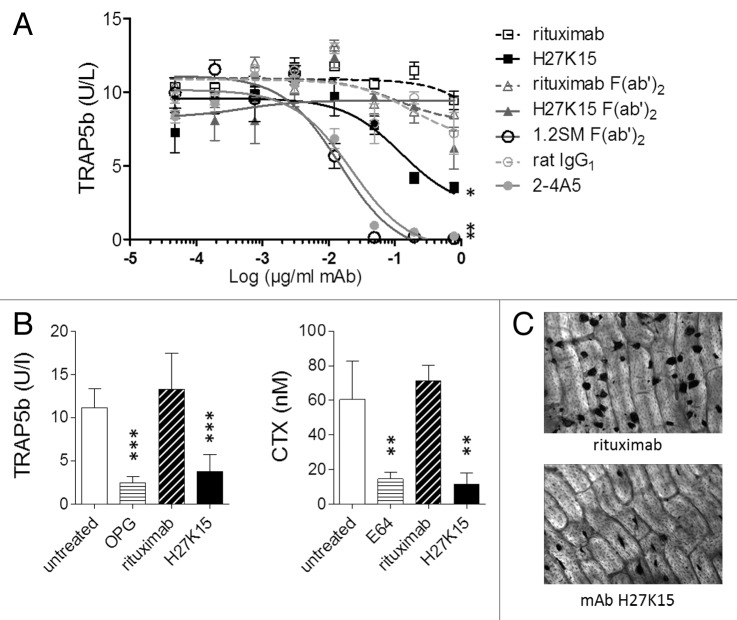
Figure 3. Effects of anti-CD115 mAbs on human osteoclast differentiation and activity. (A) Model of osteoclast differentiation from human monocytes. TRAP5b was titrated in culture supernatants from primary monocytes cultured for 8 d with CSF-1 and RANKL in the presence of graded mAb or F(ab’)2 concentrations. Three-parameter fit curves were calculated by GraphPad Prism using means +/− SEM from quadruplicate wells. Results shown were obtained from one blood donor representative of 3 tested. *: p < 0.05 using Mann-Whitney’s 2-tailed test. (B) Humanized anti-CD115 mAb H27K15 inhibits osteoclast differentiation from human CD34+ precursors and their bone resorption activity. Levels of TRAP5b (left) and CTX (right) measured following culture with 1 µg/ml H27K15 (means from 6 wells +/− SD) were compared with those obtained with 1 µg/ml of control IgG1 rituximab. Osteoprotegerin (OPG) and the cysteine protease E64 were used as reference inhibitors of osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption activity, respectively, and their effects were analyzed by comparison with untreated cultures. Results shown are from one donor representative of 4. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by t-test for comparing TRAP5b concentrations between H27K15- and rituximab-treated cultures, or with Kruskall-Wallis followed by Mann-Whitney for comparing CTX levels. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 vs. control, n = 6. (C) Representative microscopic images of the effect of mAb H27K15 on cultures from the same donor as in (B), compared with control IgG1. TRAP staining of osteoclasts differentiated on bone slices was performed after 10 d of culture with CSF-1 and RANKL in presence of the mAbs. Original microscope magnification × 100.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.