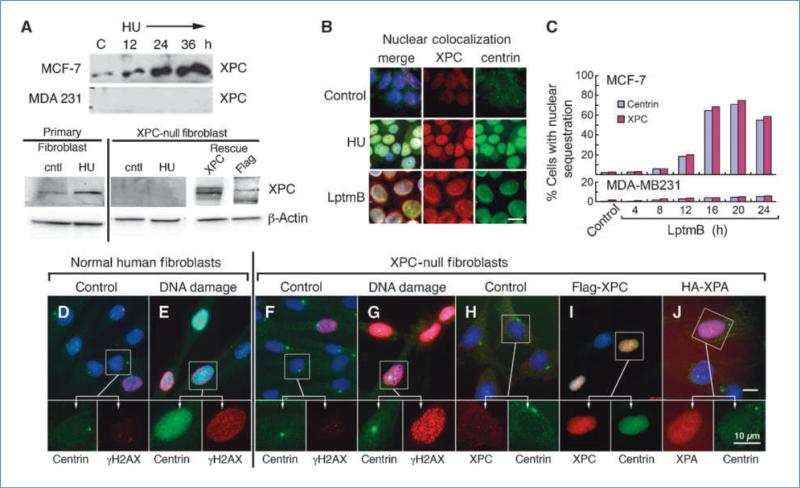
Figure 2.
Nuclear sequestration of centrin is XPC dependent. A, Western blot analysis of XPC expression in MCF-7 and MDA-MB 231 cells before and after treatment with 2 mmol/L hydroxyurea over a 36-h time course and in normal primary human fibroblasts and XPC-null human fibroblasts before and after 48-h hydroxyurea treatment and following rescue with flag-XPC. Centrin and XPC colocalize in MCF-7 nuclei following DNA damage (hydroxyurea, 48 h) or treatment with leptomycin B (LptmB; 12 h). B, nuclear colocalization of centrin and XPC following DNA damage and leptomycin B treatment. C, time course analysis for accumulation of centrin and XPC in nuclei of MCF-7 and MDA-MB 231 cells following treatment with the nuclear export inhibitor leptomycin B. Primary human fibroblasts (D and E) and XPC-null human fibroblasts (F and G) labeled for centrin (green) and γH2AX (red) before and after hydroxyurea-induced DNA damage. Note that in inset for G the centrosome lies over the nucleus. H to J, control XPC-null human fibroblasts (H) and cells transduced with lentivirus flag-XPC or HA-XPA (I and J, respectively) and labeled for centrin (green) and XPC and XPA (I and J, red). Insets in top images are enlarged below. Bar, 10 μm.