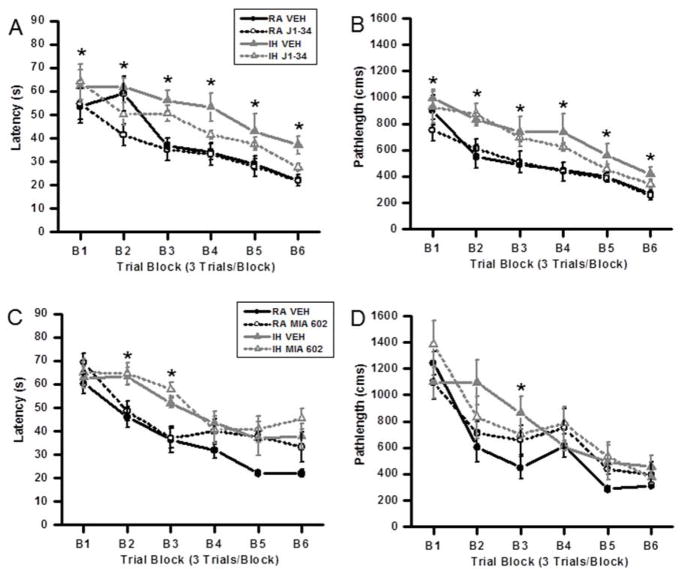
Figure 1.
Treatment with the GHRH agonist JI-34 prevents IH-induced adverse effects on acquisition of a hippocampal spatial task in the water maze in mice. Administration of the GHRH antagonist MIA-602 adversely affects spatial task learning in normoxic mice but is not additively deleterious to IH. (A, B) Mean pathlengths (cm) and latencies (seconds) to locate the target platform during spatial task acquisition during treatment with either J1-34 or vehicle, in mice exposed to either RA or intermittent hypoxia (IH). Data are mean ± SEM. (*IH-VEH vs. RA-VEH, p <0.05; One-way ANOVA). (C, D) Mean pathlengths (cm) and latencies (seconds) to locate the target platform during spatial task acquisition treatment with either MIA-602 or vehicle in mice exposed to either normoxia or intermittent hypoxia. Data are mean ± SEM. (*IH-VEH and IH-MIA 602 vs. RA-VEH, p <0.05; One-way ANOVA).