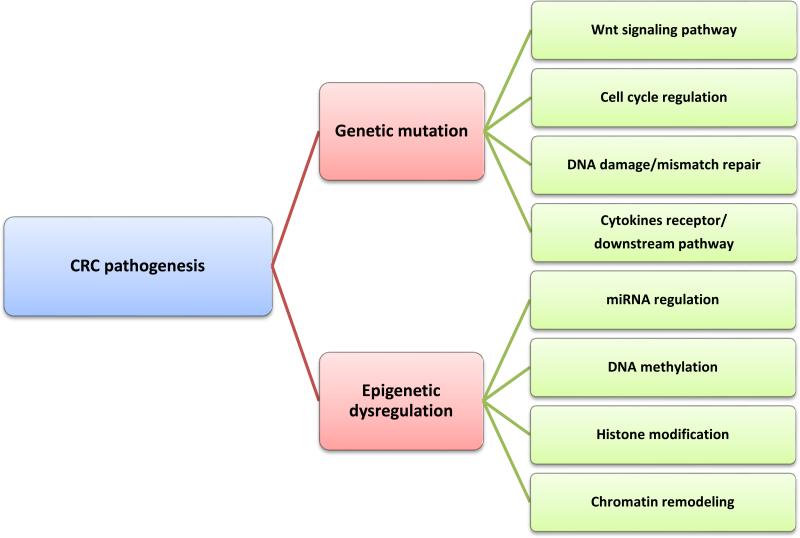
Figure 3. Genetic and epigenetic mechanisms of CRC pathogenesis.
Mutation of genes (e.g., APC) involved in the Wnt signaling pathway plays a dominant role in CRC pathogenesis. Genes that are related to cell cycle progression, DNA repair, and cytokine signaling have also been shown to be crucial for CRC pathogenesis. DNA hypermethylation of tumor suppressor gene promoter regions has been intensively studied to demonstrate its pivotal role in gene silencing. Histone modification includes histone methylation and deacetylation, both of which have been shown to be associated with DNA methylation.