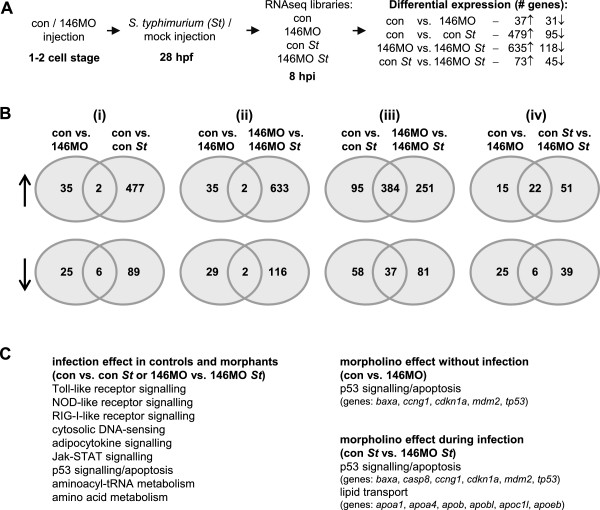
Figure 5.
Effect of combined miR-146a and miR-146b knockdown on the transcriptome response to S. typhimurium infection. (A) Experimental set-up and DESeq analysis. Embryos treated with 146a/b morpholinos or standard control morpholino were infected with S. typhimurium or mock-injected with PBS, and subjected to RNAseq at 8 hpi. DESeq was used for pairwise statistical comparison of transcript count data from the four treatment groups: control/mock (con), control/infected (con St), 146a/bMOs/mock (146MO), and 146a/bMOs/infected (146MO St). The number of genes up-regulated (↑) or down-regulated (↓) is indicated. (B) Venn diagrams showing the overlap between differentially expressed gene sets resulting from different DESeq comparisons. Top row: up-regulated genes (↑), bottom row: down-regulated genes (↓). Venn diagrams (i) and (ii) show that there was little overlap between the morpholino effect (con vs. 146MO) and the effect of infection (con vs. con St or 146MO vs. 146MO St). Venn diagram (iii) shows strong overlap in how the control and morpholino-treated groups responded to infection. Venn diagram (iv) shows the comparison between the morpholino effect in the absence (con vs. 146MO) and in the presence (con St vs. 146MO St) of infection. (C) Enrichment of signalling pathways and processes revealed by gene ontology analysis. KEGG pathway analysis was performed using DAVID v6.7 (http://david.abcc.ncifcrf.gov) [42]. Pathways linked with innate immunity and metabolism were significantly enriched by infection in both the control and morpholino treatment groups (Venn diagrams i and ii above). Pathways for p53 signalling and apoptosis were enriched due to 146MO treatment both in the absence and presence of infection (overlap group in Venn diagram iv). A set of apolipoprotein genes was significantly up-regulated by infection only in the 146MO treatment group (146MO vs. 146MO St sector of Venn diagram iii and con St vs. 146MO St sector in Venn diagram iv).