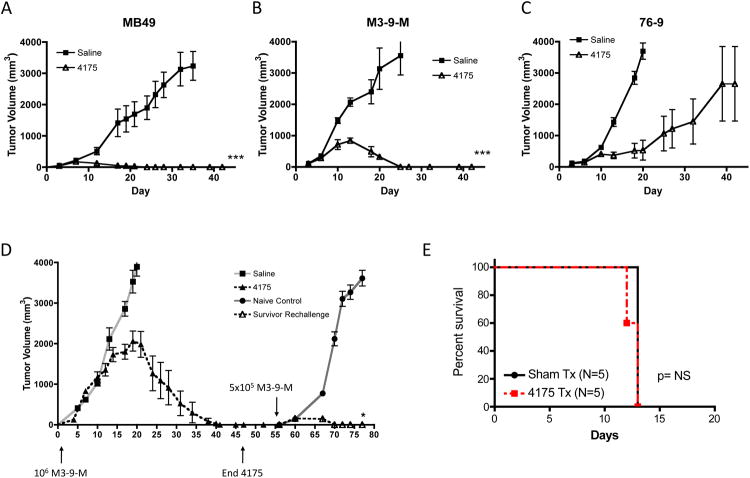
Figure 1. Early treatment with ARI-4175 induces regression in multiple tumor models and induces tumor-specific immunological memory.
(A) Female C57BL/6 mice were challenged subcutaneously with MB49 (1×106 cells) on day 0 and treated with saline or 200 μg ARI-4175 by oral gavage on days 3-7 and 10-14. Two weeks of ARI-4175 treatment produced complete regression in all mice (n=7, p<0.001). Representative of 4 independent experiments. (B and C) Female C57BL/6 mice were challenged intramuscularly with the murine RMS lines, M3-9-M (1×106 cells, n=10/group, representative of 3 independent experiments) or 76-9 (5×105 cells, n=6/group, representative of 2 independent experiments) on day 0 and treated with saline or 200 μg ARI-4175 by oral gavage on days 3-7, 10-14, and 17-21. ARI-4175 induced regression in all mice challenged with M3-9-M (B) and in 3/6 mice challenged with 76-9 (C). (D) Female C57BL/6 mice were challenged with M3-9-M as in (B) and orally dosed with ARI-4175 on days 3-7. Treatment resumed on day 14 and continued on a schedule of 5 days treatment with 2 days rest until day 42 when the mice exhibited complete tumor regression. On day 56, mice were rechallenged with M3-9-M (5×105 cells) in the opposite leg. With no further treatment following rechallenge, ARI-4175-treated survivors exhibited initial tumor growth followed by rejection, indicative of immunological memory, whereas M3-9-M grew rapidly in naïve controls. * p<0.05, ***p<0.01 Representative of 2 independent experiments. (E) Rag1-/- mice were challenged with M3-9-M (1×105 cells, n=5/group) and treated with saline or 200 μg ARI-4175 by oral gavage on days 3-7 and 10-14 as in figure (B).