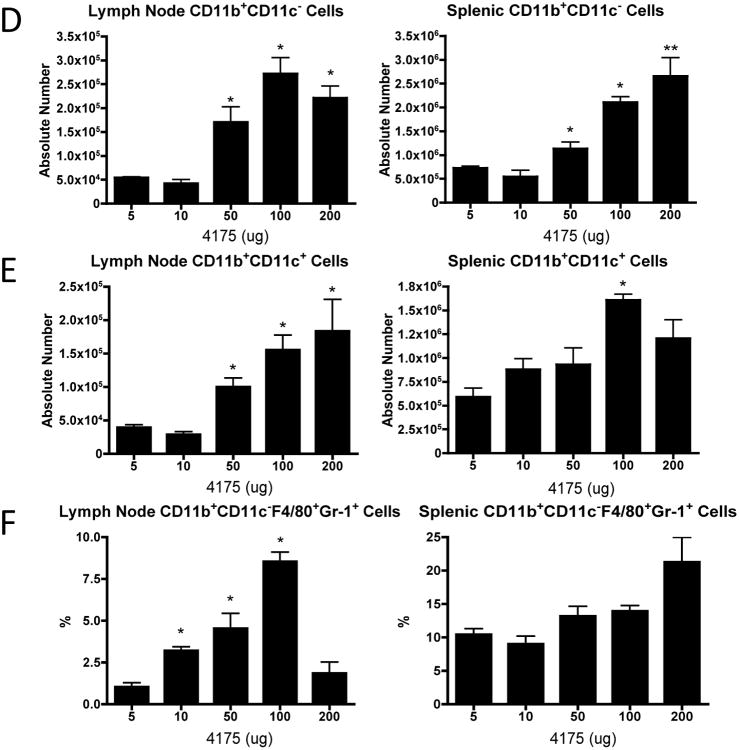
Figure 3. ARI-4175 induces dose-dependent anti-tumor activity and myeloid cell expansion in lymph nodes.
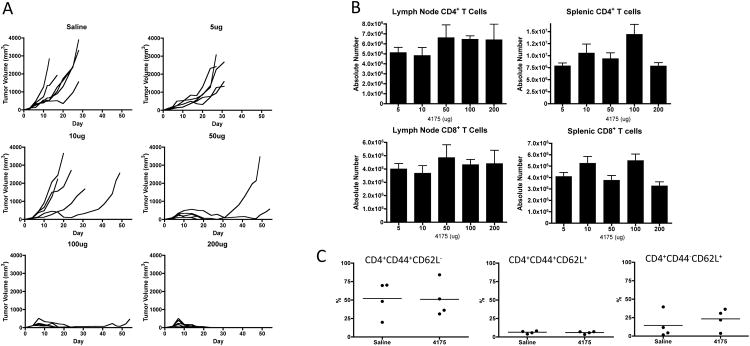
Following subcutaneous MB49 challenge (106 cells), C57BL/6 mice were gavaged with saline (n=6) or ARI-4175 at doses: 5 μg, 10 μg, 50 μg, 100 μg, or 200 μg (n=5-6/group). (A) Individual tumor curves demonstrate anti-tumor activity of ARI-4175 at doses of ≥ 50 μg without noticeable toxicity. (B-E) C57BL/6 mice were orally gavaged as described in (A), sacrificed on day 11, and tissues were harvested, processed, and stained for FACS analysis. Absolute number of CD4+ or CD8+ T cells (B) or phenotype of CD4 + T cell subsets (C) were not altered by ARI-4175 treatment. (D and E) Myeloid cells (CD11b+CD11c-) and mDCs (CD11b+CD11c+) showed dose-dependent increases in lymphoid tissues of ARI-4175 treated mice. (F) F4/80+Gr-1+ myeloid cells increased in frequency in a dose-dependent manner in lymph nodes, but not in spleens, of ARI-4175-treated mice. * p<0.05, **p<0.01. Data representative of 2 (Figure 3B-F) or 4 (Figure 3A) experiments.