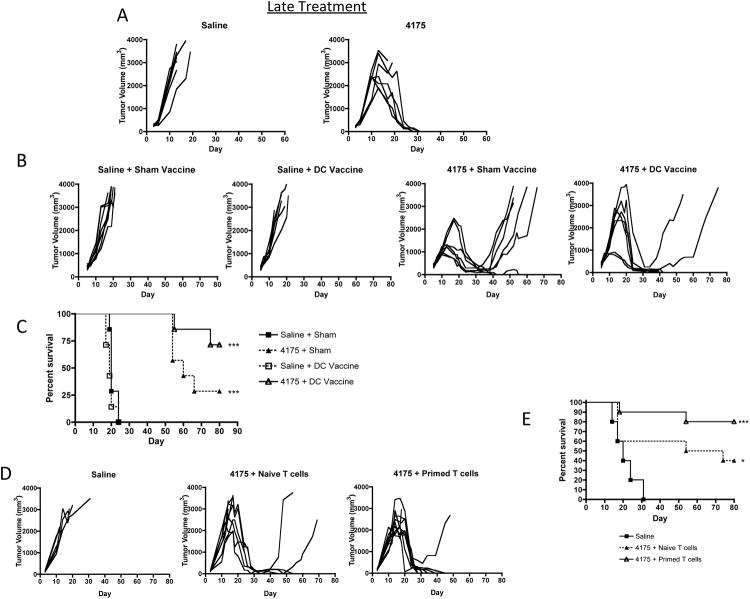
Figure 5. Inhibition of established M3-9-M tumors by ARI-4175 in combination with DC vaccination or ACT.
(A) Individual tumor-growth curves in female C57BL/6 mice that were challenged intramuscularly with M3-9-M (1×106 cells) on day 0. Treatment with 200 μg ARI-4175 started on day 10 when tumors were well established, and ended on day 42. Although two ARI-4175-treated mice had to be euthanized around day 20 due to large tumor burden, tumors in the remaining mice regressed completely and did not recur after termination of treatment. Data representative of 3 independent experiments. (B and C) M3-9-M challenge and ARI-4175 treatment follow the schedule described in (A), except that ARI-4175 treatment was discontinued one week earlier on day 35. An RPMI sham- or a DC-vaccine (106) was administered intraperitoneally on day 14. (B) Individual tumor curves demonstrating eradiation of tumors in 2/7 mice with ARI-4175 alone and 5/7 mice with a combination of ARI-4175 and DC vaccination. There was no effect with DC vaccination alone. (C) Survival plot showing significantly improved survival with ARI-4175 alone or ARI-4175 plus vaccine (both <0.001 compared to saline). The survival between the ARI-4175+DC Vaccination was significantly improved compared to ARI-4175 plus sham vaccination (p<0.05). Data representative of 2 independent experiments. (D and E) M3-9-M challenge and ARI-4175 treatment follow the same schedule described in (B and C). T cells (5.7×106) from either primed or naïve donors were administered IV by tail vein injection on day 10. (D) Individual tumor curves show complete regressions in 5/10 mice treated with ARI-4175 and naïve T cells and in 8/10 mice treated with ARI-4175 and primed T cells. (E) When compared with saline controls, both ARI-4175 treated groups had significantly improved survival compared to saline (p<0.05 for ARI-4175 plus naïve T cells vs saline and p<0.001 for ARI-4175 plus primed T cells vs saline), however the difference between these groups was not significant. Data representative of 2 independent experiments.