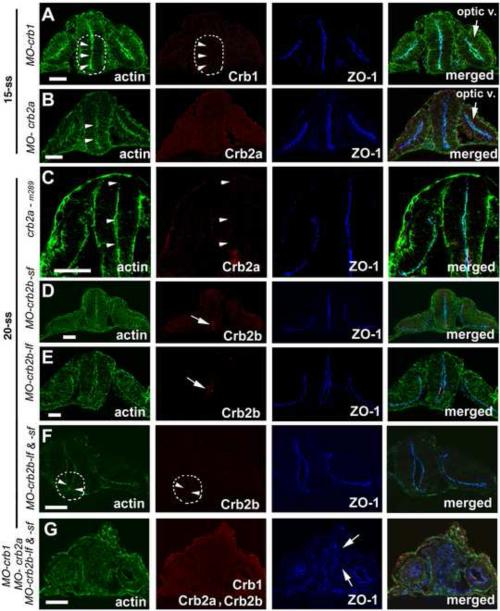
Figure 4.
Individual loss of Crb1, Crb2a, and Crb2b function did not disrupt the neuroepithelial polarity at 15-ss and 20-ss as evidenced by proper localization of apical makers ZO-1 and the actin bundles (arrowheads). A-B. Morpholino suppression of either Crb1 (A) or Crb2a (B) expression did not interrupt the proper apicobasal polarization of diencephalon neuroepithelium at 15-ss. The dashed line circles the ventral brain region where Crb1 should otherwise be expressed in wildtype. C. crb2am289 mutational deficiency of Crb2a did not affect the apicobasal polarity of the diencephalon (C) at 20-ss. D-F. Morpholino suppression of Crb2b-lf (E) and Crb2b-sf (D) or both Crb2b-lf and Crb2b-sf (F) did not affect the apicobasal polarity of the ventral diencephalon neuroepithelium where Crb2b-lf and Crb2b-sf are otherwise expressed (encircled by a dashed line) at 20-ss in wildtype. Arrows indicate the supposed expression of Crb2b-lf and Crb2b-sf in corresponding embryos treated with individual morpholinos against crb2b-sf and crb2b-lf, respectively. G. Simultaneous suppression of Crb1, Crb2a, and Crb2b led to the mislocalization of apical markers ZO-1 (arrows) and actin bundles in the diencephalon at 20-ss. The lack of Crb1, Crb2a and Crb2b immunostaining demonstrated the effectiveness of expression suppression by the morpholinos. “Optic V.” for optical vesicle; Scale bars, 50 ! m.