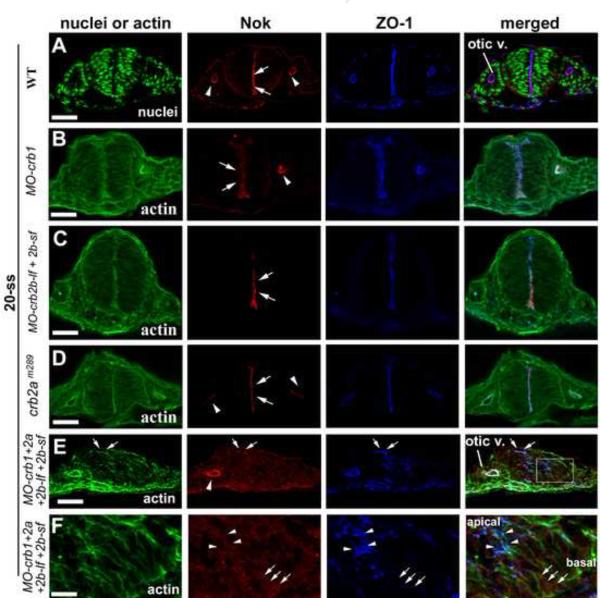
Figure 6.
The localization of Nok and Crb1, Crb2a, and Crb2b relies on each other in the central nervous system but not in the otic vesicle. A. Nok localizes to the apical surfaces of the hindbrain neuroepithelium (arrows) and the otic vesicle (arrowheads) in wildtype at 20-ss. B-D. Individual loss of Crb1 (B), Crb2b (C), and Crb2a (D) did not affect the apical localization of Nok in the hindbrain (arrows) and the otic vesicle (arrowheads). E. Simultaneous suppression of Crb1, Crb2a, and Crb2b disrupted proper apicobasal polarization of the hindbrain neuroepithelium and Nok localized diffusely in the neural rod. By contrast, the apical localization of Nok in the otic vesicle (arrowhead) was not affected. Arrows indicate some occasional ZO-1 positive structures that also show some low level of Nok signals. F. A boxed region in panel E was magnified four times to show the biased distribution of ZO-1 in the apical end of the epithelium (arrowheads) compared to the basal ends (arrows). By contrast, there was no clear difference in Nok distribution between apical end and the basal end. “Otic V.” for otic vesicle; Scale bar, 50 ! m (A-E) and 12 ! m (F).