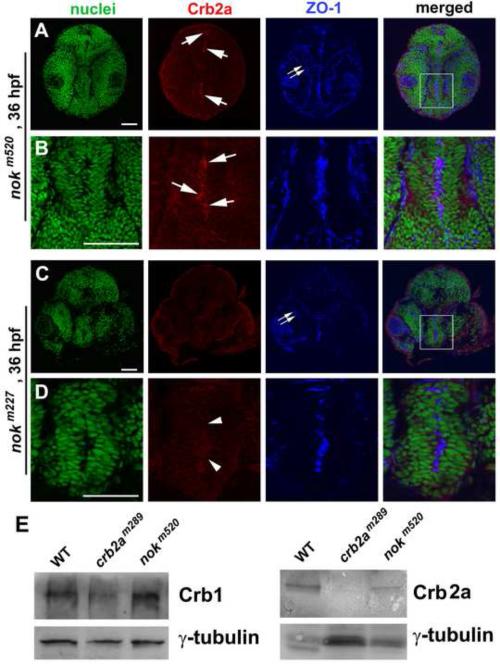
Figure 8.
Crb2a localized to the apical surface of certain regions of the diencephalon neuroepithelium in nokm520 mutants but not in nokm227 mutants at 36 hpf. A, B. Arrows indicate the local enrichment of Crb2a at the apical surfaces of certain regions of the diencephalon in nokm520 mutants. A boxed region in panel A is enlarged in panel B. C, D. Arrowheads indicate the corresponding apical surfaces of the diencephalon in nokm227mutants, showing the lack of apical enrichment of Crb2a. A boxed region in panel C is enlarged in panel D. The apical markers ZO-1 localized ectopically to the interior of the retina (double arrows), as expected in nok mutants (A, C). The nuclei were stained with TO-PRO (green). Scale bar, 50 ! m. E. Western blotting analyses of protein expression at 30 hpf detected Crb1 in both nokm520 and crb2am289 mutants as well as Crb2a in WT and nokm520 but not in crb2am289 mutants. ! -tubulin blotting was used as loading controls. Please note that even though there are variations in ! -tubulin loading control signals for the Crb2a blotting (likely due to sample lose during preparation), our conclusion that certain level of Crb2a is present in nokm520 mutant embryos still stands.