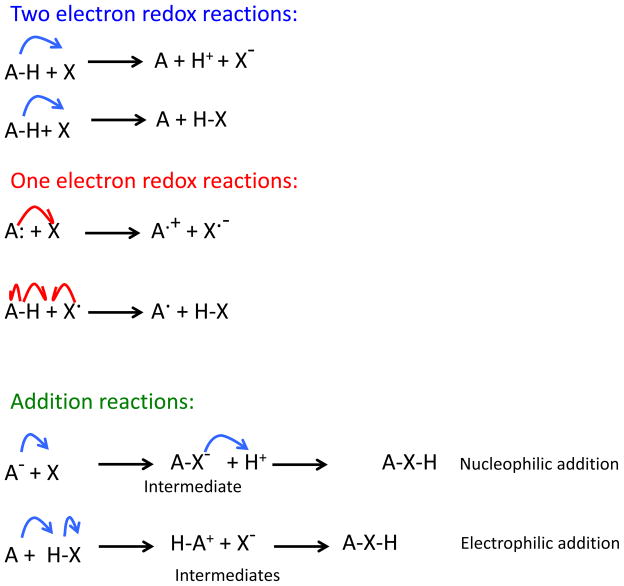
Fig 1.
Oxidation. Nucleophile give electrons in two electron (blue curved arrows) or one electron (red curved arrows) reactions without forming an adduct. Reductants (HA) are nucleophiles that give one or two electrons to an oxidant (X), without forming an adduct. The transfer of electrons in oxidations and reduction may involve a hydrogen atom (H·) in one-electron reactions or a hydride (H:) in two electron reactions. Nucleophiles can also add to electrophiles thereby forming covalent bonds in either electrophilic or nucleophilic addition reactions.