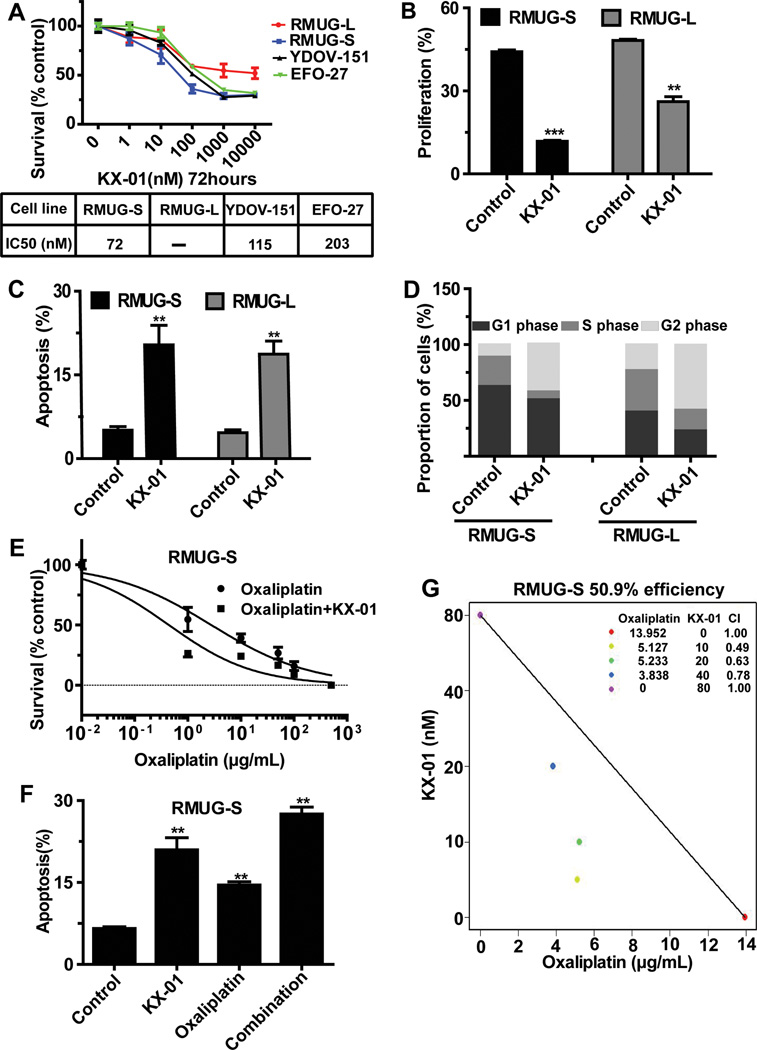
Figure 2.
Biological effects of KX-01 on mucinous ovarian carcinoma cells in vitro. (A) MTT assay results showing the effect of KX-01 on cell survival at various concentrations in a panel of mucinous ovarian carcinoma cells. Cell survival was calculated as the number of cells surviving relative to the number of cells surviving in the control group. IC50 indicates median inhibitory rate. (B) EdU assay results showing inhibition of cell proliferation in cells treated with KX-01 compared with control cells in RMUG-S and RMUG-L cells. (C) Annexin V and 7-aminoactinomycin D assay results showing cell apoptosis in cells treated with KX-01 compared with control cells in RMUG-S and RMUG-L cells. (D) Flow cytometry results showing induction of mitotic arrest in cells treated with KX-01 compared with control cells in RMUG-S and RMUG-L cells. (E) Cell cytotoxicity in RMUG-S cells treated with various concentrations of oxaliplatin with or without 100nM KX-01 for 72 hours. Results are presented as in A. (F) Isobologram analysis for the combination of KX-01 and oxaliplatin in RMUG-S cells. The interaction index was <1 at all examined points. (G) Apoptosis in RMUG-S cells after treatment with 15 µg/mL oxaliplatin, 100nM KX-01, or a combination of both treatments for 72 hours. All experiments were repeated at least 3 times, and bars represent means with standard errors. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 compared with the control group.